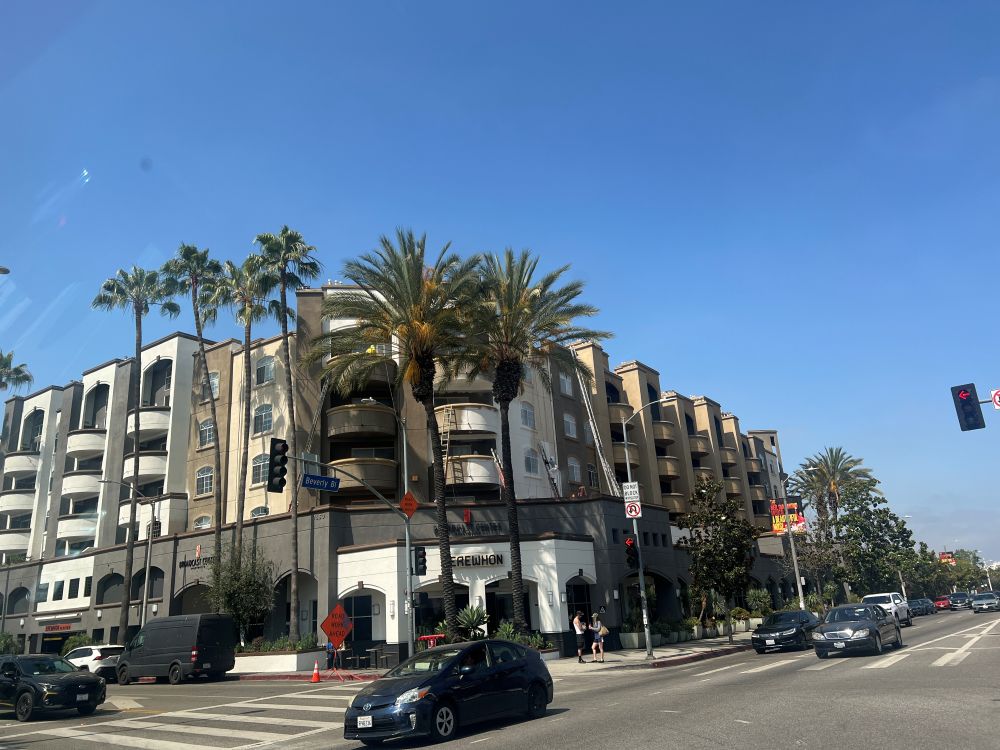
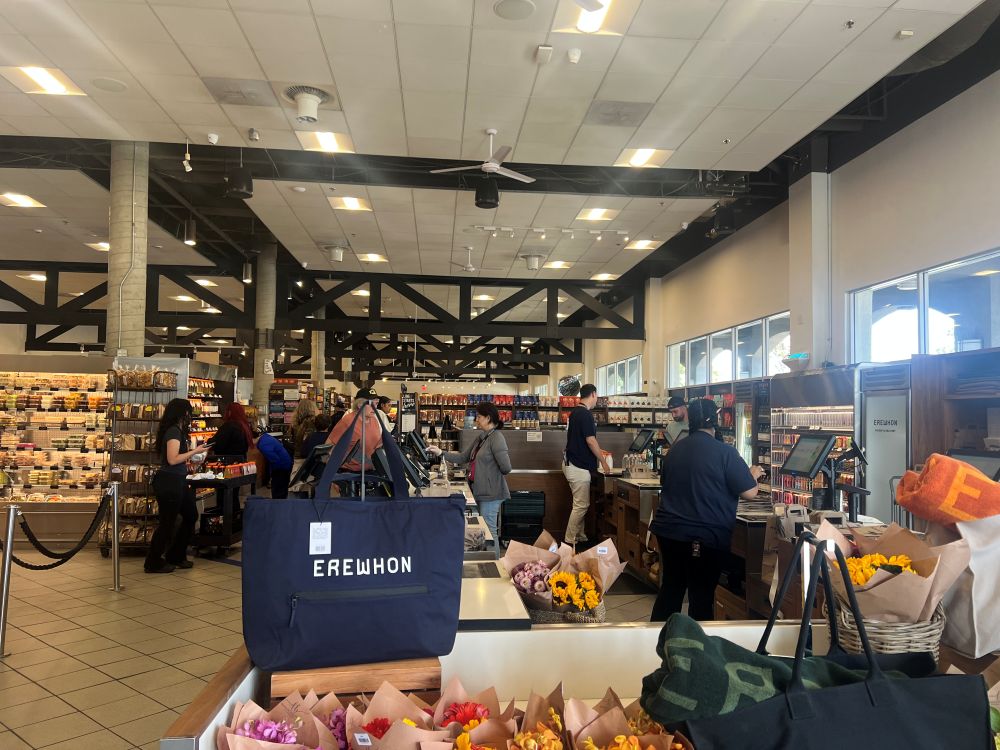
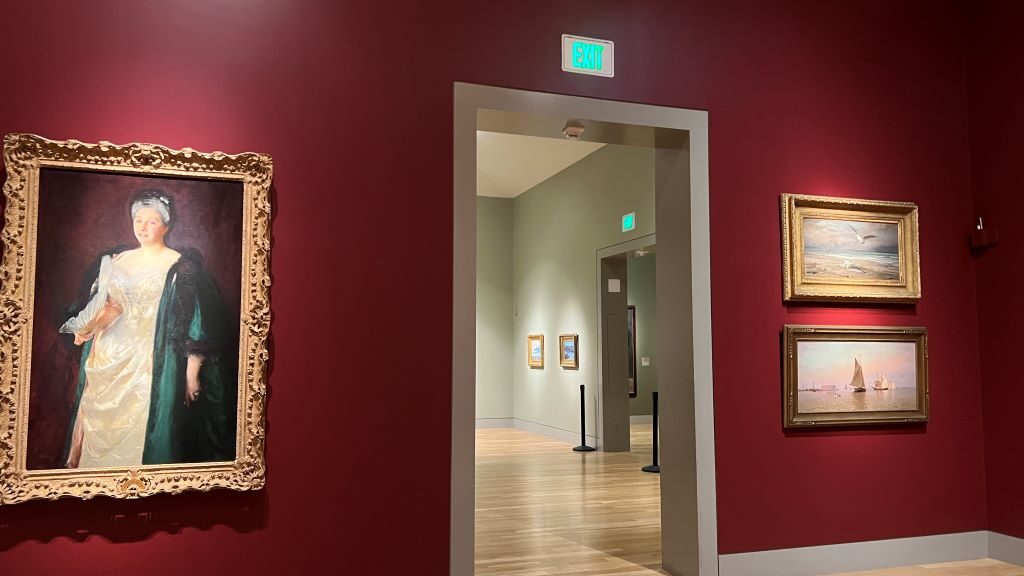
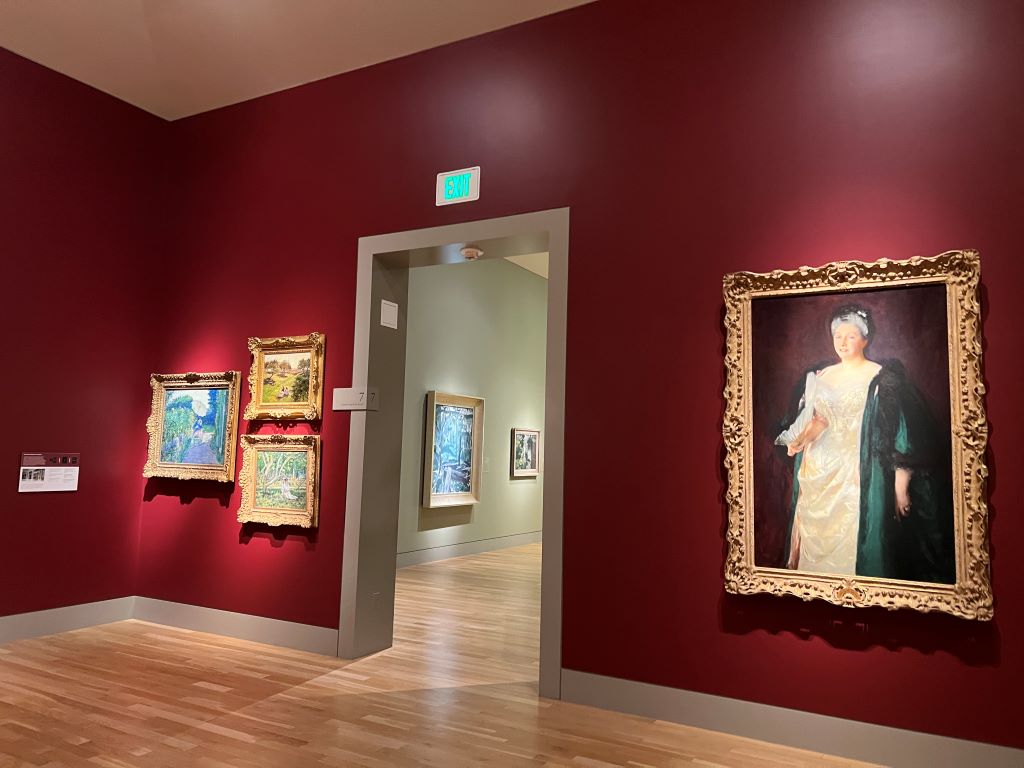
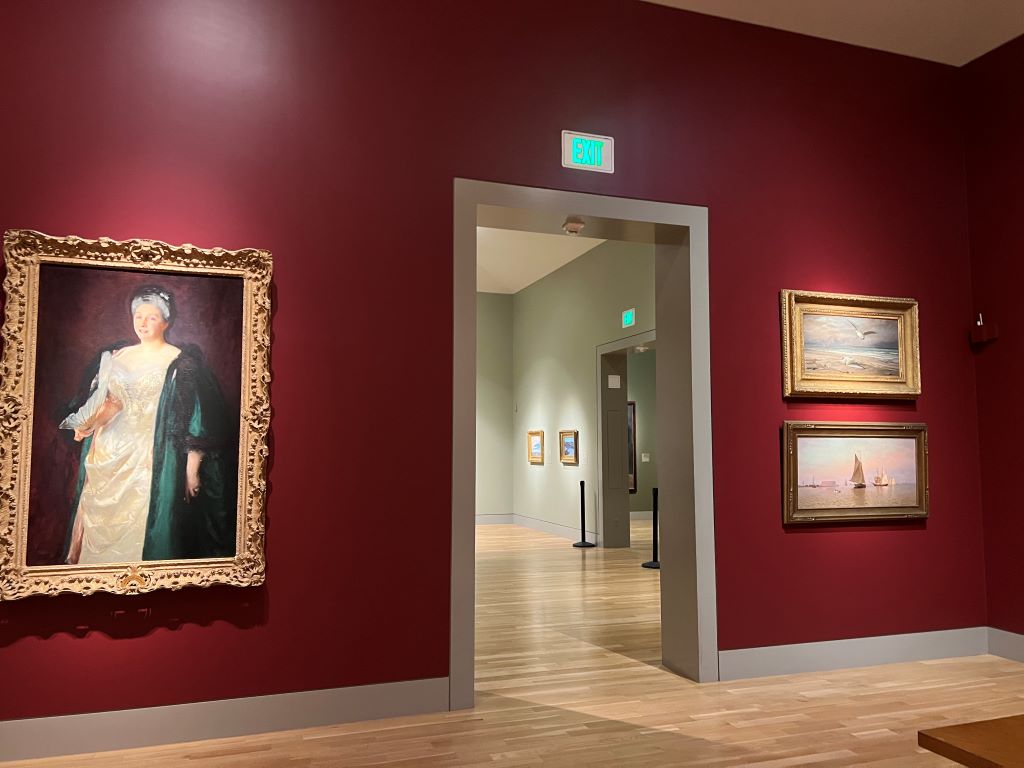
I visited one Erewhon store in Los Angeles. Erewhon is known as the most expensive grocery store in the world. All items are organic or health-focused, and many are linked to celebrities or wellness influencers.


The smoothies are expensive and some are named after Hailey Bieber or Travis Scott. Even a small sushi wild tuna roll costs $14.
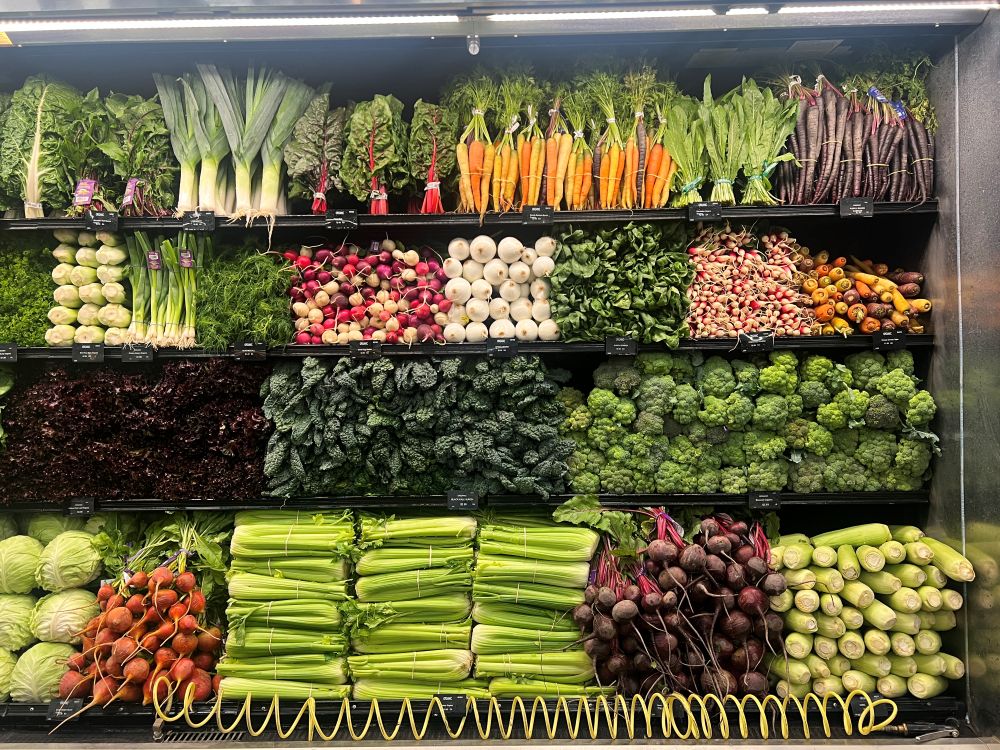

But what surprised me more was how carefully the vegetables were displayed. Each carrot and leaf was perfectly lined up. It looked almost like a vegetable museum. This kind of display, along with sustainable ingredients and celebrity hype, might help customers feel the price is worth it.

Erewhon’s name comes from a novel where people are punished for being sick. The store also seems to say that my health is my responsibility. With its careful curation and premium feel, Erewhon gives me the feeling that I am doing something good for myself.
***
Reference
Haws, K. L., Reczek, R. W., & Sample, K. L. (2017). Healthy diets make empty wallets: The healthy= expensive intuition. Journal of Consumer Research, 43(6), 992-1007.
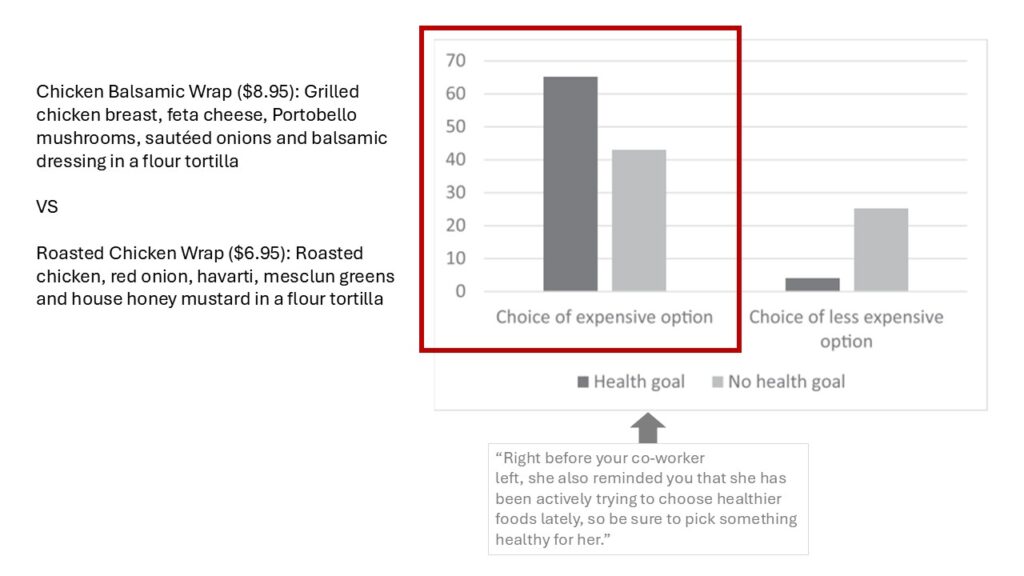
Understanding consumer decision making about what to eat is both complex, as multiple factors can drive food choice, and important, as food choice impacts overall health. This research examines an intuition at the crossroads of two important criteria for food decision making—healthiness and price—finding that consumers believe that healthier food is more expensive than less healthy food. While this relationship may be accurate in some cases, consumers overgeneralize this belief to contexts and product categories where it is not objectively true. As a result, the healthy = expensive intuition influences consumer decision making by impacting inferences of missing attributes and choice between alternatives. Further, consistent with dual process models, the intuition acts as a bias in shaping how consumers process information about health and price when consumers are processing heuristically, including altering both perceptions of how “healthy” a given ingredient is as a function of product price and the amount of information search consumers engage in when evaluating health claims, such that consumers have a higher standard of evidence when evaluating intuition-inconsistent claims. Overall, the healthy = expensive intuition has a powerful influence on consumer decision making, with significant implications for both consumers and marketers.