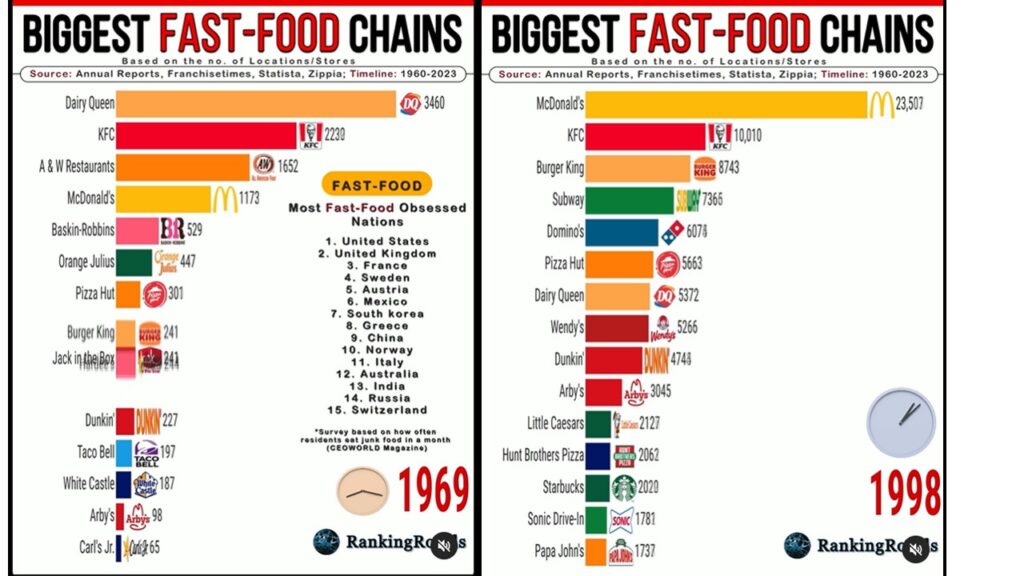
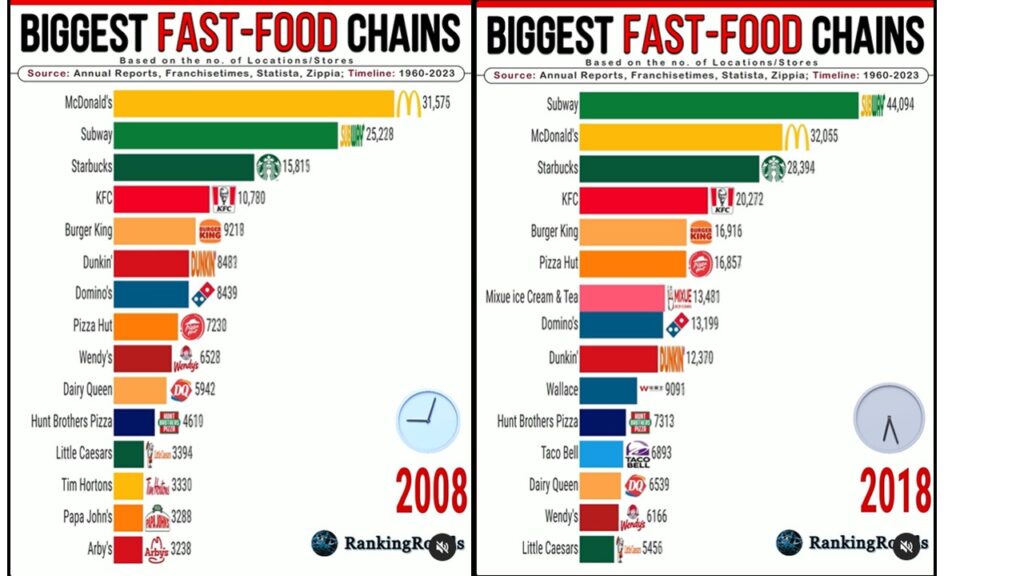
Tim Hortons, a Canadian coffee brand, is as iconic to Canada as maple syrup and hockey. It offers free coffee to police officers, making these stores a safe places for night snack lovers. Its reach even extends beyond borders; there was a store in Afghanistan, serving coffee and Timbits to Canadian soldiers who long for a taste of home.
Recently, Tim Hortons expanded into Korea. It successfully kept many core offerings including the most popular coffee called Double Double. However, the chain overlooked the importance of sugar, a key ingredient of coffee, running into some challenges with brand authenticity.
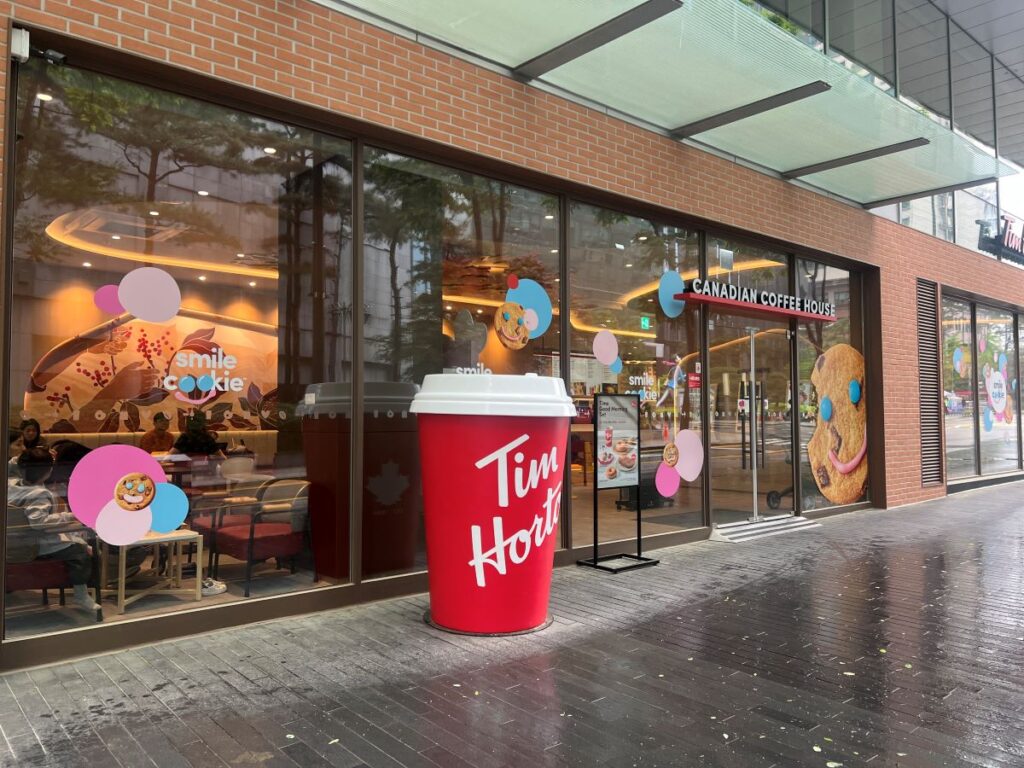

When I ordered my once favorite “a black coffee with two sugars” at a freshly opened store in Korea, I was served coffee with two Korean sugar packets. Unfortunately, they differ from the familiar Canadian sugars that are part of the authentic Tim Hortons experience. This seemingly minor change impacts the unique experience that loyal Tim Hortons customers like me expect.

Brands should consistently deliver on their promises to maintain authenticity (Schallehn et al. 2014). For global brands like Tim Hortons, preserving even the smallest elements of their identity is key. Deviations from established brand expectations—such as using different ingredients or local adaptation—can diminish consumer trust and loyalty, even if those changes seem insignificant.
***
Reference
Schallehn, M., Burmann, C., & Riley, N. (2014). Brand authenticity: Model development and empirical testing. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 23(3), 192-199.
Purpose
The purpose of this paper is to develop a model of brand authenticity and analyze the antecedents and effects of the construct. Although there is no doubt about the relevance of authenticity in personal relationships, published research has yet not thoroughly explored the concept’s meaning in reference to brands.Design/methodology/approach
Based on socio-psychological attribution theories and grounding on the identity-based brand management approach, a causal model of brand authenticity is developed. The hypothesized relationships are analyzed using the partial-least-squares approach. The primary data are based on an online survey conducted in Germany (n = 600). The respondents were asked about fast-food and beer brands.Findings
The data show that brand authenticity positively impacts on brand trust. Furthermore, the key antecedents in the model (consistency, continuity and individuality of a brand) drive the perception of brand authenticity as hypothesized.Research limitations/implications
The model should be tested in further product categories and moderators should be integrated.Originality/value
The findings suggest that authenticity is perceived when a brand is consistent, continuous and individual in its behavior. Nevertheless, the empirical results indicate that the factor individuality has the lowest influence on perceived brand authenticity. This is an interesting finding, as being “unique” is commonly regarded as an important success factor in branding. Although the study’s findings confirm its relevancy, they relativize its importance: being consistent, meaning that a brand fulfills its brand promise at every brand-touch point, and being continuous, meaning that the brand promise reflects the essential core of the brand, are of major importance.