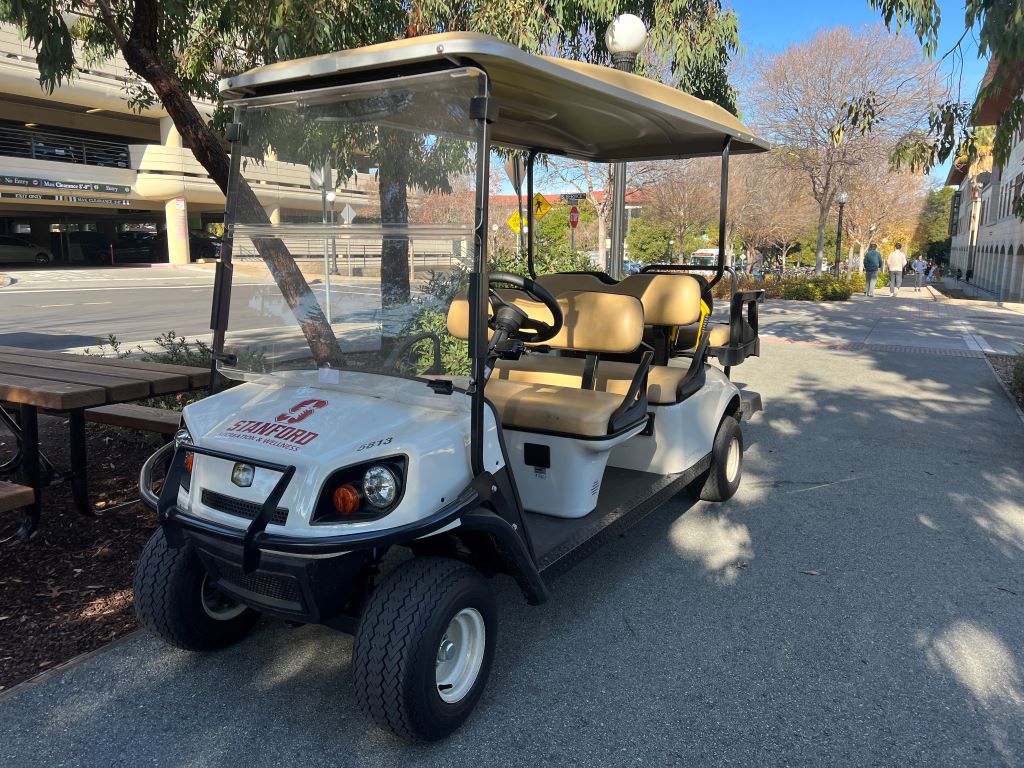
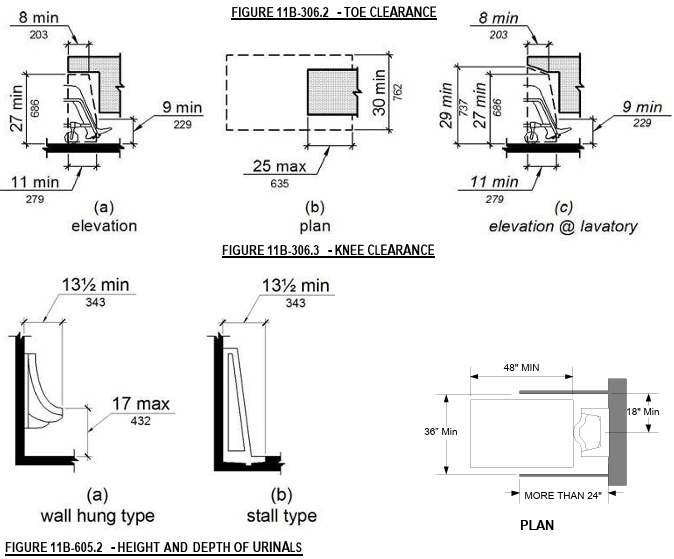
When I first saw golf carts at Stanford, I was very surprised. It felt like I was not at a university but on a golf course. Seeing these small vehicles moving around campus made me excited. They looked fun, and the atmosphere felt more relaxed.
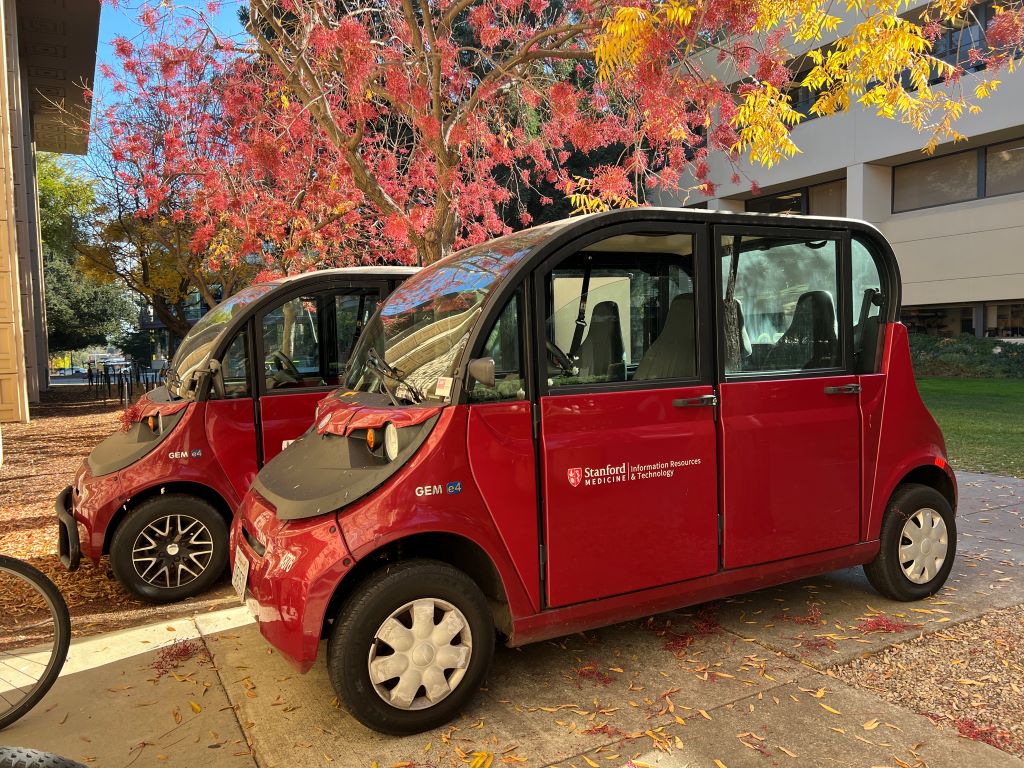

Later, I learned that some of these carts are designated for students who hurt their ankles. Stanford has a special service called DisGo Cart Service to help people who have difficulty walking. They are also used for many purposes, such as helping people with disabilities, supporting medical staff, and moving faculty members quickly.
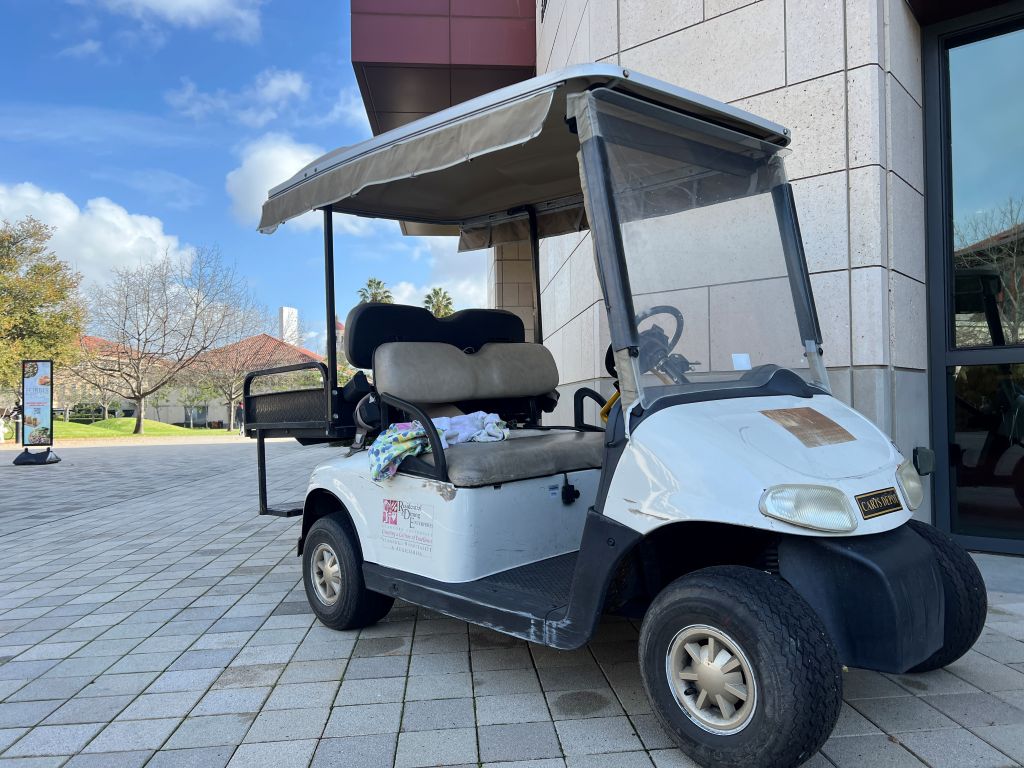

Other universities might use golf carts for similar purposes. However, because Stanford’s campus is very large, these carts are common, making them feel like a normal part of life here.
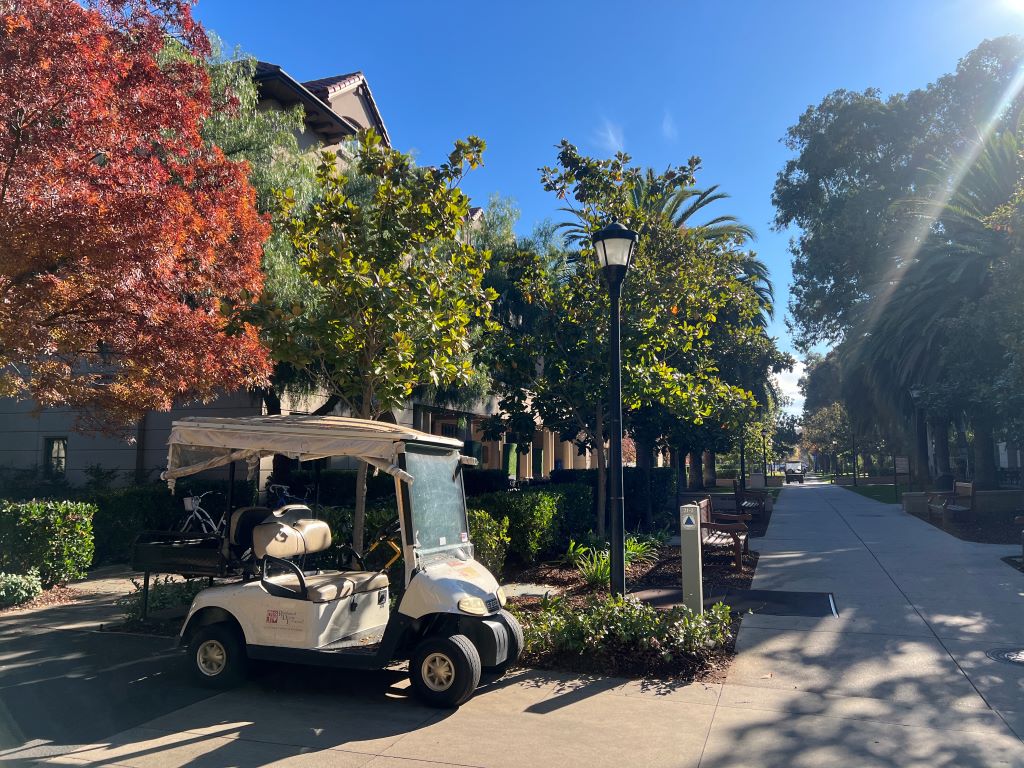

New students may feel this effect when they first arrive, but after some time, they get used to it. Even now, when I see these carts, I feel like I am in an exciting place.
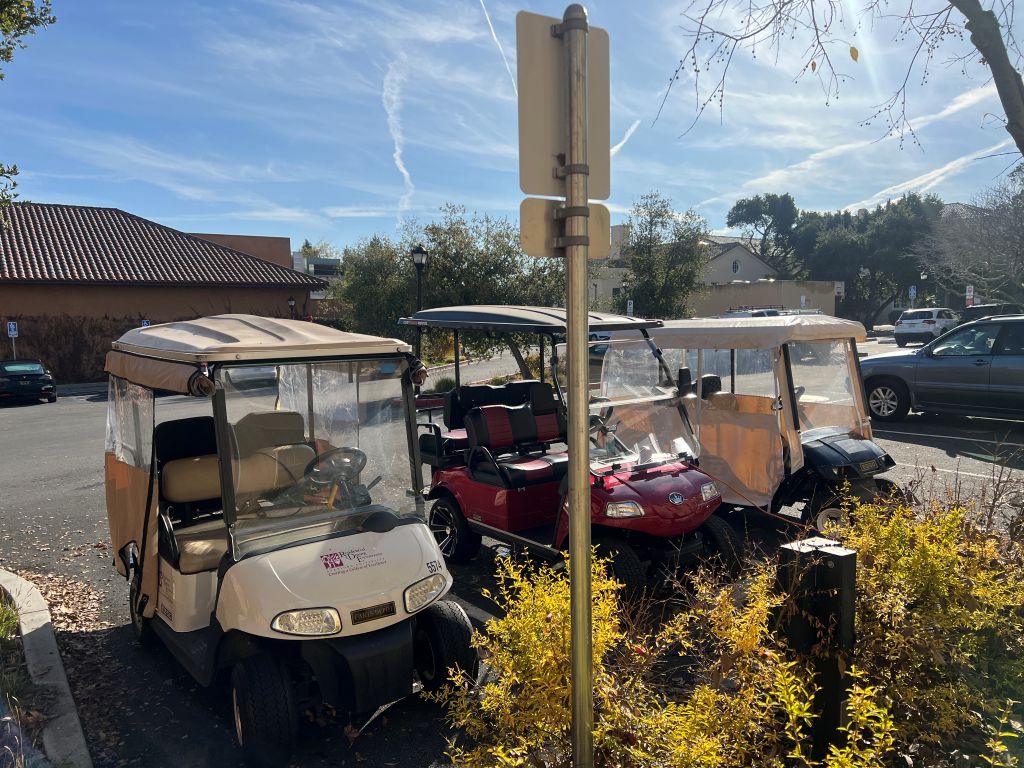
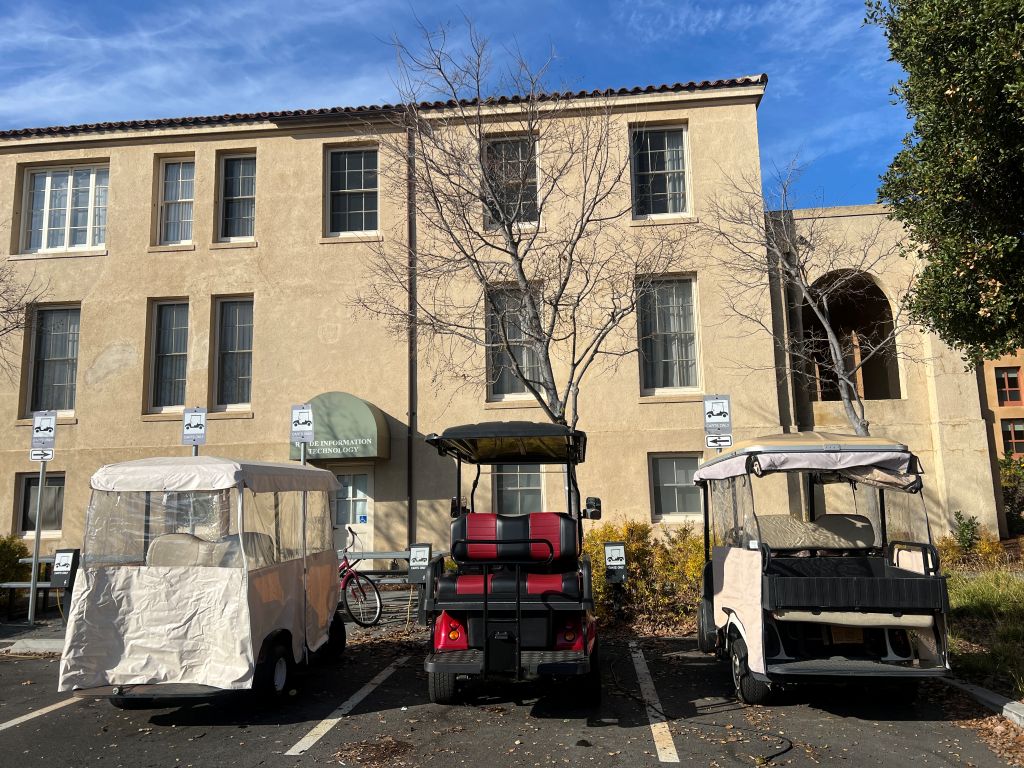


When golf carts line up in parking spots, they remind me of a group of cats sitting quietly. Their backside is cute; they look like the back of cats because the small roofs and rounded shapes create a soft, compact appearance.
***
Reference
Fredrickson, B. L. (2001). The role of positive emotions in positive psychology: The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. American psychologist, 56(3), 218.
In this article, the author describes a new theoretical perspective on positive emotions and situates this in perspective within the emerging field of positive psychology. The broaden-and-build theory posits that experience of positive emotions broaden people’s momentary thought–action repertoires, which in turn serves to build their enduring personal resources, ranging from physical and intellectual resources to social and psychological resources. Preliminary empirical evidence supporting the broaden-and-build theory is reviewed, and open empirical questions that remain to be tested are identified. The theory and findings suggest that the capacity to experience positive emotions may be a fundamental human strength central to the study of human flourishing.