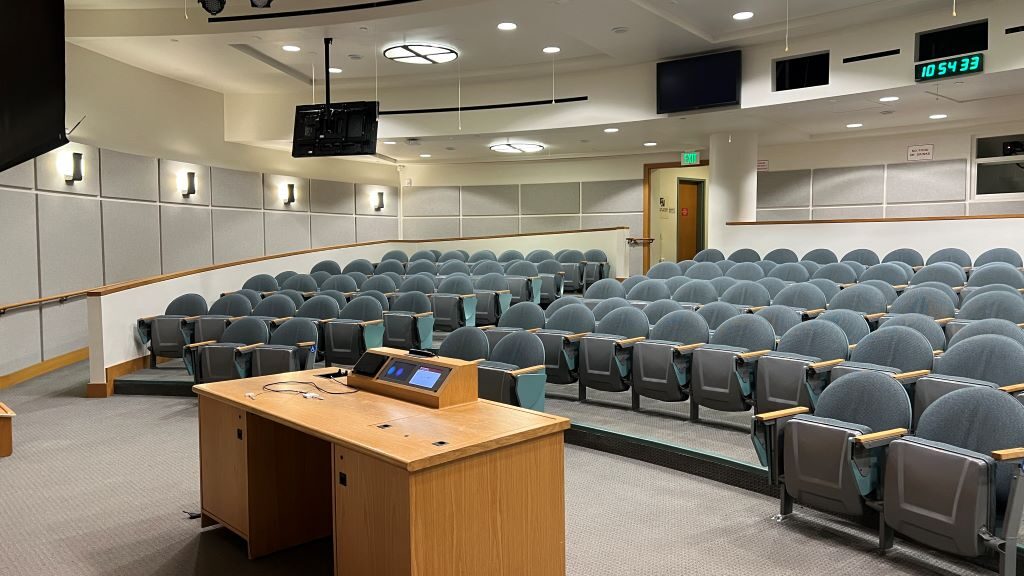
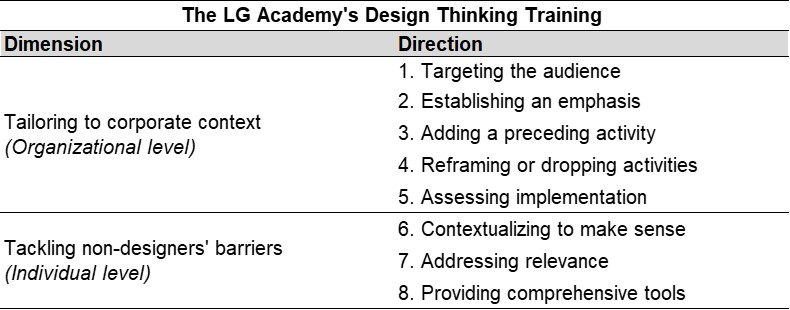
Walking into the empty classroom in Stanford’s Gates Building, I was struck by its resemblance to a boutique movie theater. The whole green chairs are arranged in the semi-circular way and all face a central screen. The muted colors and soft lighting added to this ambiance, making the space feel more like a private screening room.
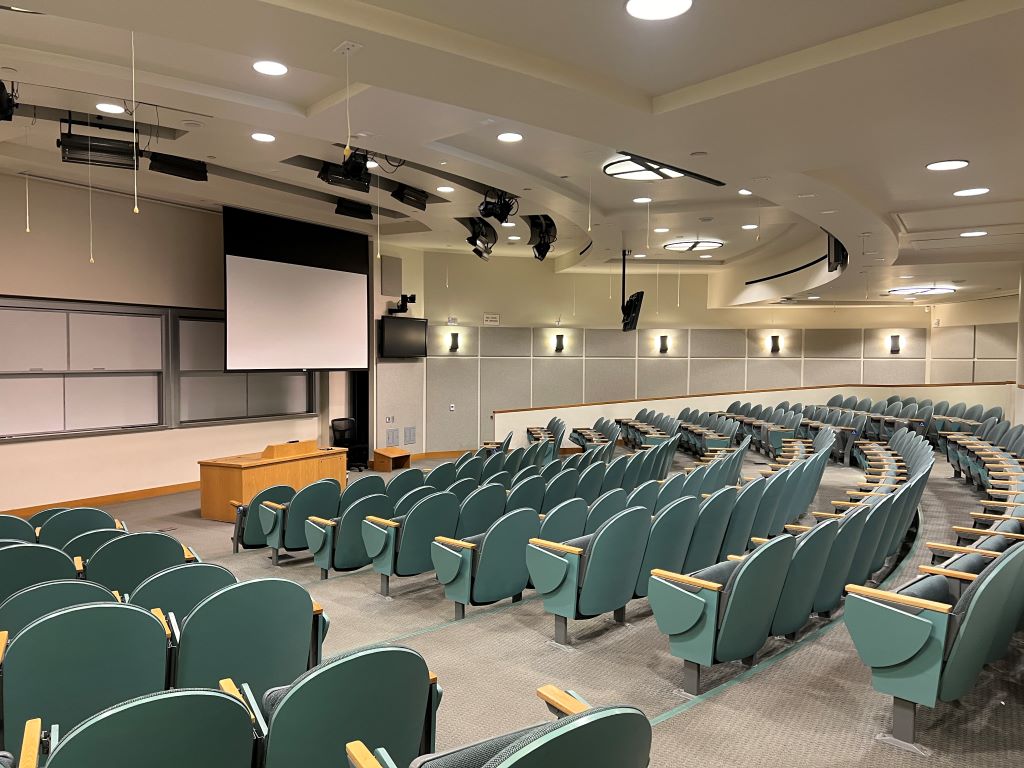

This theater-like design can influence both teaching and learning positively. For instructors, the semi-circular seating fosters more and better interaction with students. For students, such layouts can help them follow presentations and participate in discussions actively.
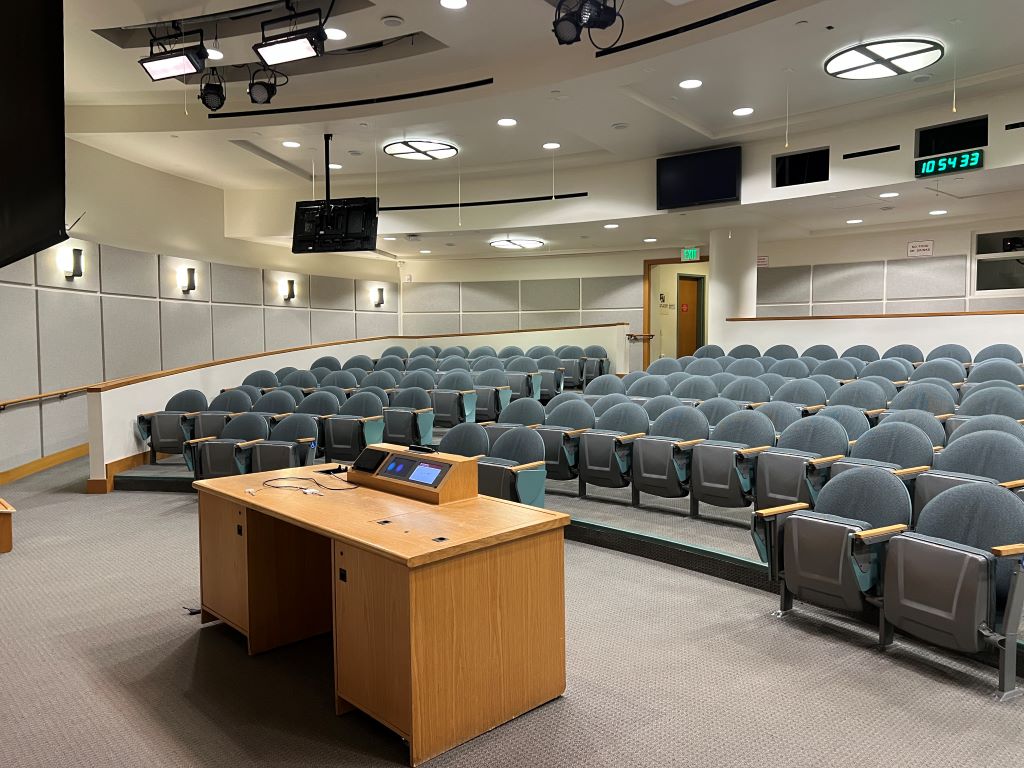

Research shows that classroom designs resembling theaters, with tiered seating and central focal points, can increase student engagement and satisfaction. Indeed, classroom environments that mimic theater designs can enhance learning experiences by promoting interaction and focus.
***
Reference
Cheryan, S., Ziegler, S. A., Plaut, V. C., & Meltzoff, A. N. (2014). Designing classrooms to maximize student achievement. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1(1), 4-12.
Improving student achievement is vital for our nation’s competitiveness. Scientific research shows how the physical classroom environment influences student achievement. Two findings are key: First, the building’s structural facilities profoundly influence learning. Inadequate lighting, noise, low air quality, and deficient heating in the classroom are significantly related to worse student achievement. Over half of U.S. schools have inadequate structural facilities, and students of color and lower income students are more likely to attend schools with inadequate structural facilities. Second, scientific studies reveal the unexpected importance of a classroom’s symbolic features, such as objects and wall décor, in influencing student learning and achievement in that environment. Symbols inform students whether they are valued learners and belong within the classroom, with far-reaching consequences for students’ educational choices and achievement. We outline policy implications of the scientific findings—noting relevant policy audiences—and specify critical features of classroom design that can improve student achievement, especially for the most vulnerable students.