Joo, J., Lee, A. J., & Park, J. H. (2018). A New Framework of Design Management and Three Additional Requirements To Apply Design Management to Korean Companies: Experience Design, Collaboration, and Trial and Error. Design Convergence Study, 17(6), 145–165.
The present research has two objectives. First, we introduce a new framework of design management proposed by Heather Fraser, the Director of Rotman Designworks. It comprises three gears: (1) user understanding, (2) concept visualization, and (3) strategic business design. Second, we investigate the key requirements that are necessary to apply the new framework to Korean companies. We collected fifty reports about the five special lectures from a new product development course at a university in Korea. These lectures were given by three designers and two product managers. We used interpretative analysis and followed three process of qualitative analysis of transcription, coding, and theme discovery. We derived specific requirements for applying design management to Korean companies: (1) experience design, (2) collaboration, and (3) trial and error. We introduced a novel design management framework and clarified the requirements how to successfully apply it to Korean companies. These findings imply that, firstly, executives and practitioners need to improve mutual communication and, secondly, corporations and agencies respect each other in their partner relationships.
Keywords
Collaboration, Design Management, Design Thinking, Experience Design, Trial and Error

“In sum, our review of the past research on design management shows various approaches introducing design into chronological business management and supporting successful business cases. However, it focuses design management in the strategic stage; it does not provide specific assistance with practitioners who are interested in applying design management in their tasks. Therefore, we introduce a model for practitioners to undertake management planning efficiently” (pg. 150)
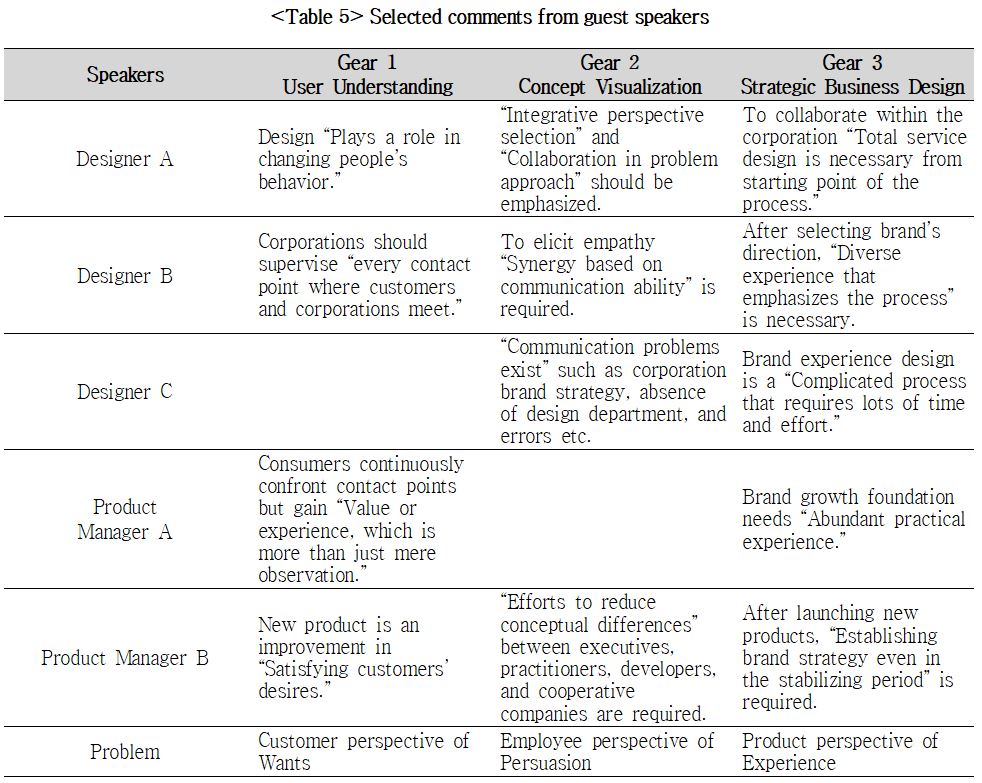
“…we should accept the meaning of designing the customer experience, which includes the company’s identity, rather than emphasizing the product’s design-centered simple styling. … respect is required in partner relationship of corporations and agencies. In order to activate design management, the corporation’s interior decision-making and organization structure should change” (pg. 162)