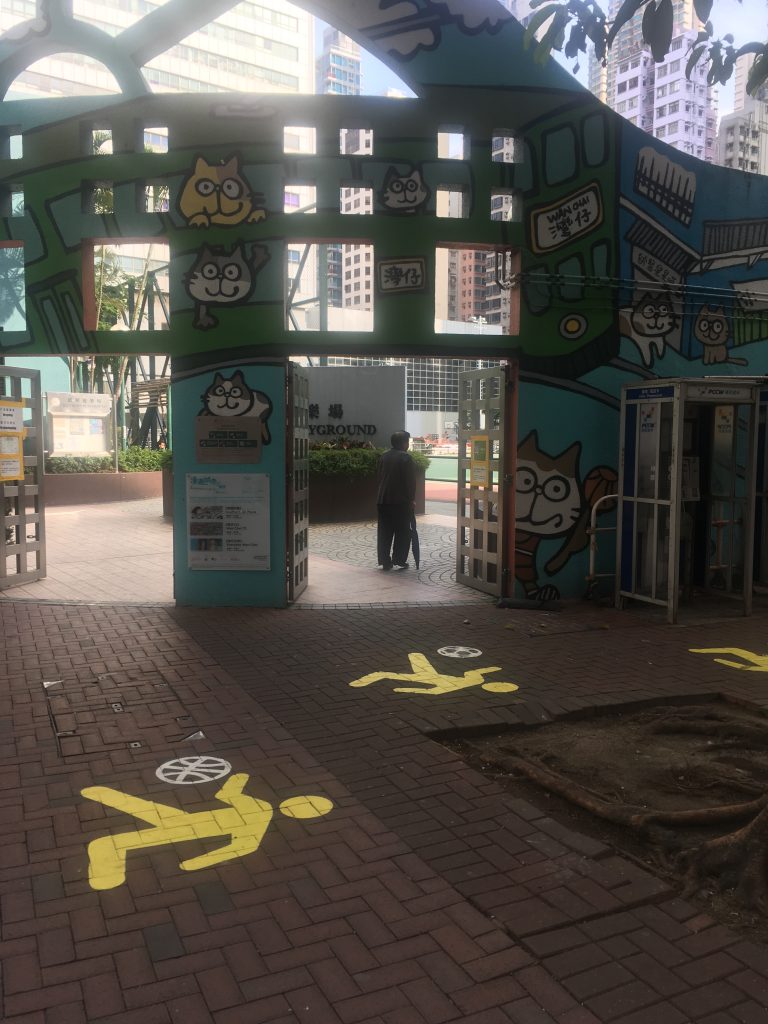
Most street signs ask someone NOT to do something. For instance, they ask pedestrians not to run fast or they ask drivers not to drive fast.
However, at a school in Hong Kong, I finally met different street signs designed for students. They encourage students to DO something. Several yellow students were painted on a street surrounding a tree. They are encouraged or at least allowed to carry different items such as basketball, football, soda, and noodle (?).
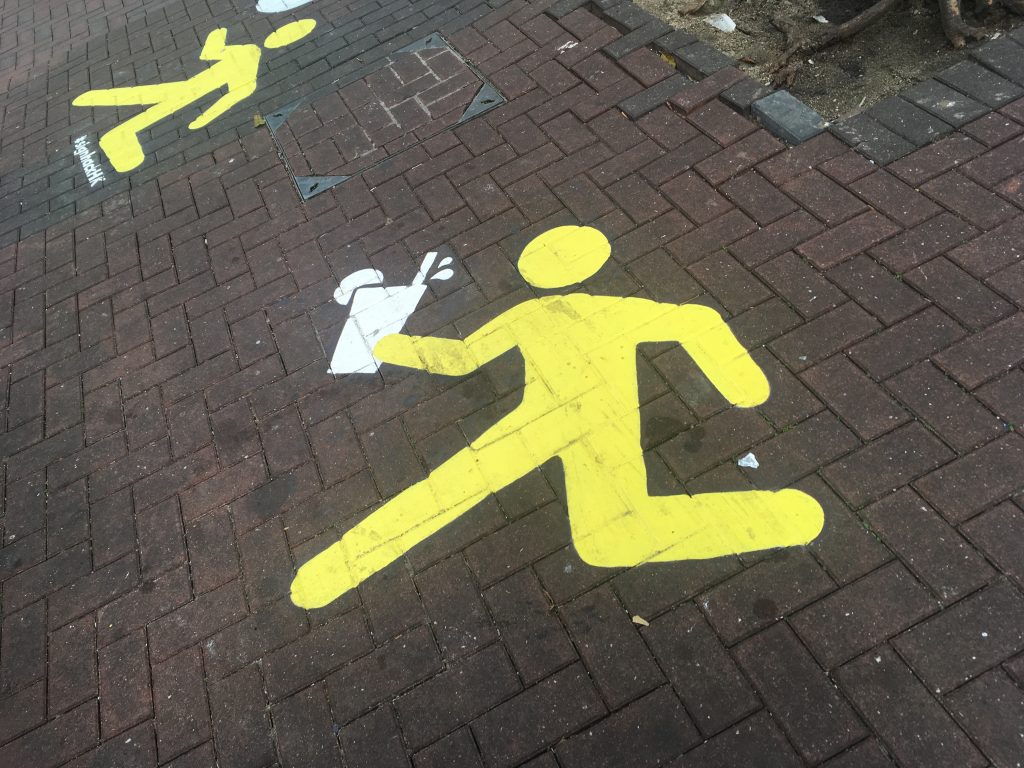
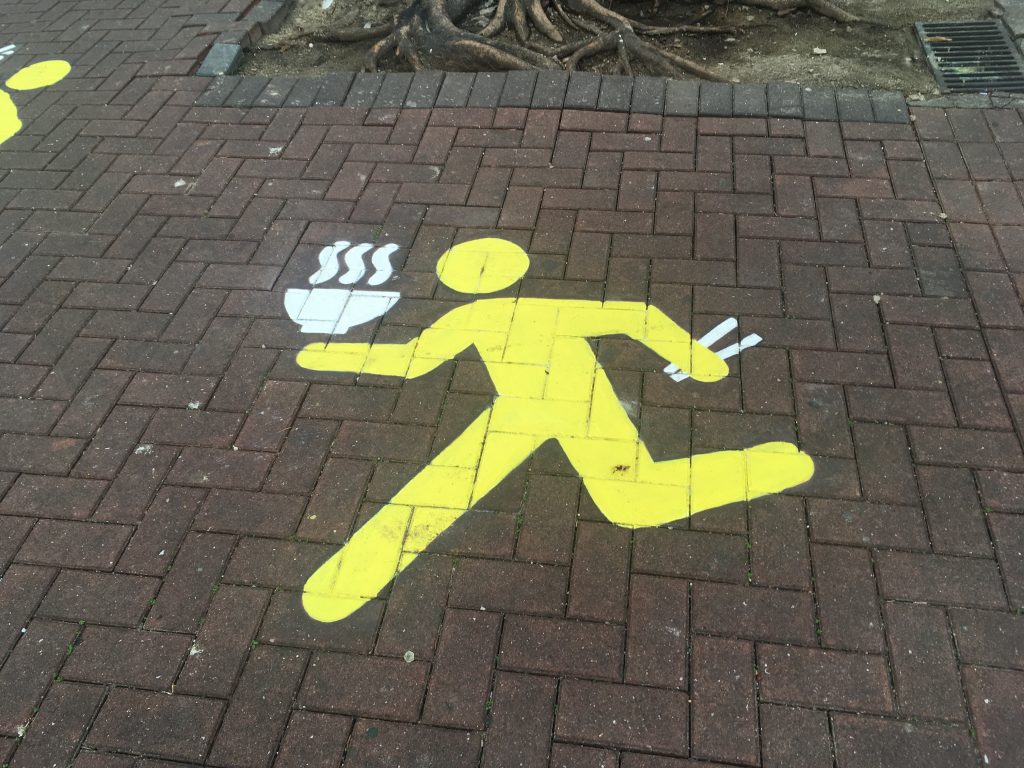



Research suggests that we behave differently when we are in a promotion-focused mode than in a prevention-focused mode. If we see promotion-focused street signs more on the road, we behave differently (e.g., please fly drone here or please use mobile phone here).
***
Reference
Trope, Y., & Liberman, N. (2010). Construal-Level Theory of Psychological Distance. Psychological Review, 117(2), 440–463.
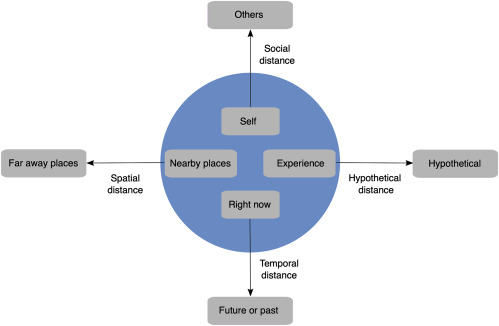
People are capable of thinking about the future, the past, remote locations, another person’s perspective, and counterfactual alternatives. Without denying the uniqueness of each process, it is proposed that they constitute different forms of traversing psychological distance. Psychological distance is egocentric: Its reference point is the self in the here and now, and the different ways in which an object might be removed from that point—in time, in space, in social distance, and in hypotheticality—constitute different distance dimensions. Transcending the self in the here and now entails mental construal, and the farther removed an object is from direct experience, the higher (more abstract) the level of construal of that object. Supporting this analysis, research shows (a) that the various distances are cognitively related to each other, (b) that they similarly influence and are influenced by level of mental construal, and (c) that they similarly affect prediction, preference, and action.