Piknic, a unique building in Seoul, hosted an exhibition of a British designer Jasper Morrison. The title of the exhibition was THINGNESS.
For the hundredth anniversary of the Bauhaus, piknic presents an exhibition offering a general introduction to the world of British designer and modernist interior Jasper Morrison, who has created a sensation with his “Super Normal” philosophy. Born in London in 1959 and studied Design at Kingston Polytechnic and the Royal College of Art in London, with a one-year scholarship to the HDK design school in Berlin in 1984. Morrison is considered one of the most important designers of our era, holding supreme status in his field since establishing his studio in 1986 at the age of 27 and working with such distinguished companies such as Vitra, Littala, Muji, and Samsung. Focusing in everything from small daily essentials like knives and forks to the public transportation systems of cities, he places no limits on the areas where he works. As they share in the design journey of someone who has created a wide variety of objects related to human life, we hope all our visitors will find their answer to the question of what constitutes a “Good Thing” – and what makes a “Good Life.”
I found from the brochure that Jasper Morrison and Naoto Fukasawa designed an exhibition in 2006, which called attention to design management. Indeed, Naoto Fukasawa appeared in this website thanks to his electronic products such as Muji CD player and his paper products under the name of SIWA.
I participated in a guided tour led by a female “docent.” Although I did neither plan for it nor pay for it, she shared with us interesting story about each work. Listening to why and how each work has been completed enriched the whole tour experience.
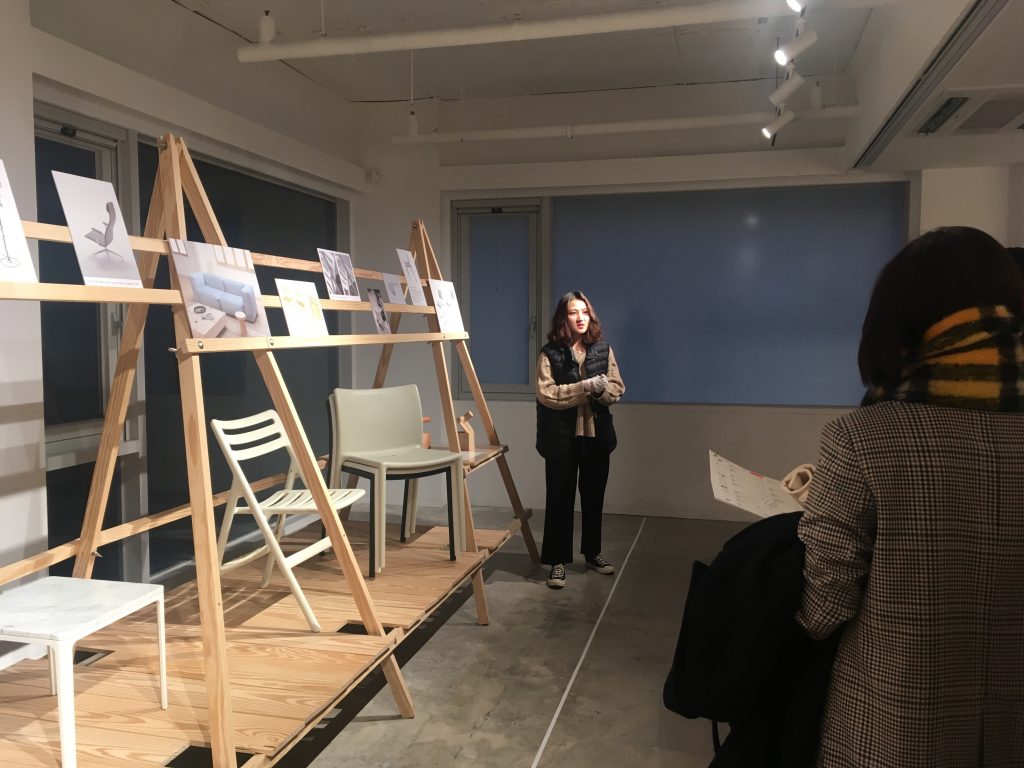
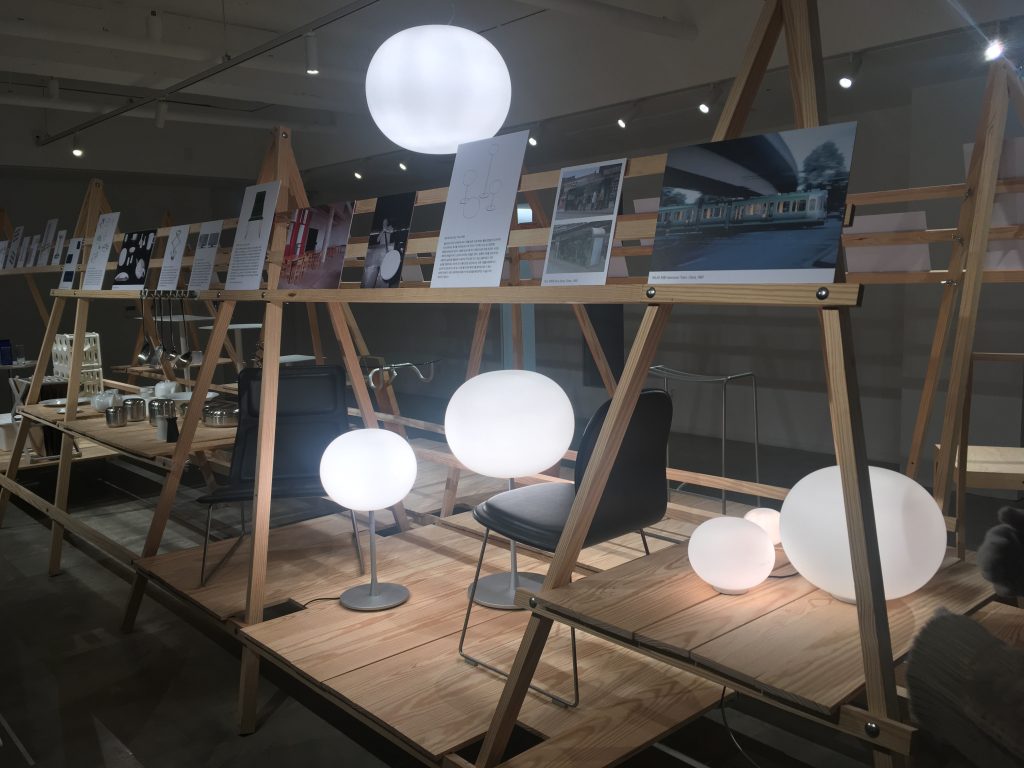


He has made a wide variety of products including chair, lighting, kitchen utensil, and home care products. My favorite was the cork side table. Although the docent highlighted the functional feature of the cork which naturally repels termites, I was simply fascinated by how it looks. It reminded me of a wine cork.


***
Reference
Joy, A., & Sherry, J. F. J. (2003). Speaking of Art as Embodied Imagination: A Multisensory Approach to Understanding Aesthetic Experience. Journal of Consumer Research, 30(2), 259–282.
This article focuses on somatic experience–not just the process of thinking bodily but how the body informs the logic of thinking about art. We examine the links between embodiment, movement, and multisensory experience insofar as they help to elucidate the contours of art appreciation in a museum. We argue that embodiment can be identified at two levels: the phenomenological and the cognitive unconscious. At the first level, individuals are conscious of their feelings and actions while, at the second level, sensorimotor and other bodily oriented inference mechanisms inform their processes of abstract thought and reasoning. We analyze the consumption stories of 30 museum goers in order to understand how people move through museum spaces and feel, touch, hear, smell, and taste art. Further, through an analysis of metaphors and the use of conceptual blending, we tap into the participants’ unconscious minds, gleaning important embodiment processes that shape their reasoning.