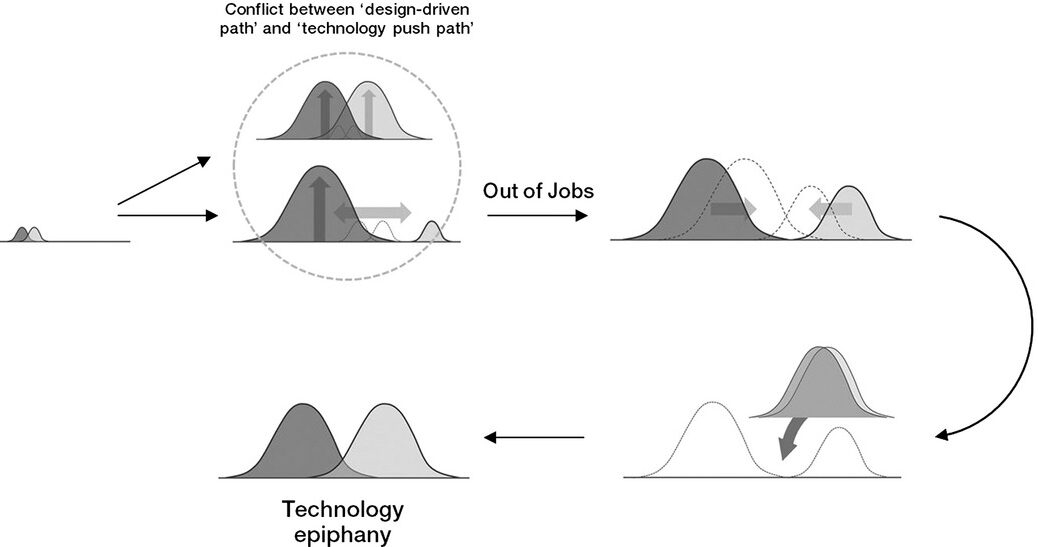
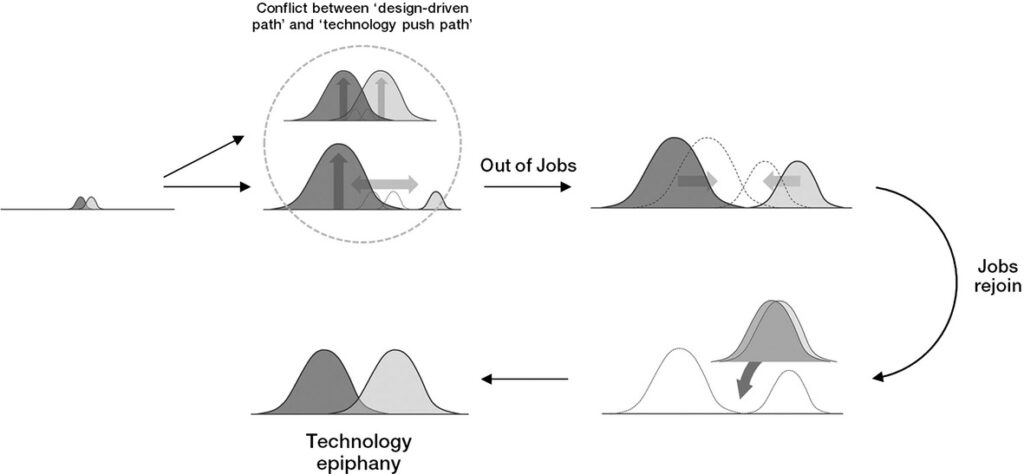
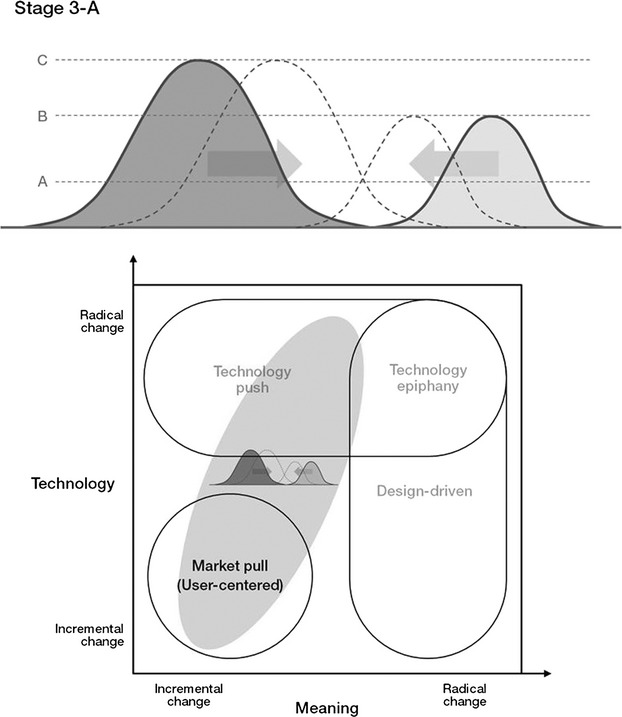
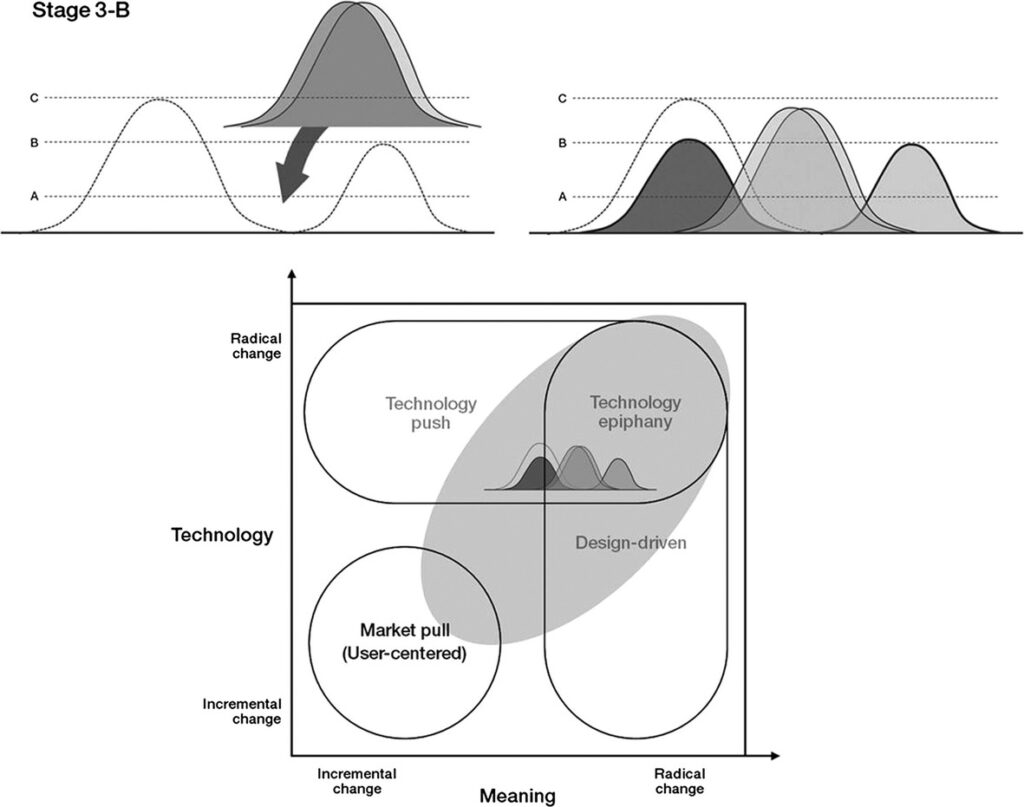
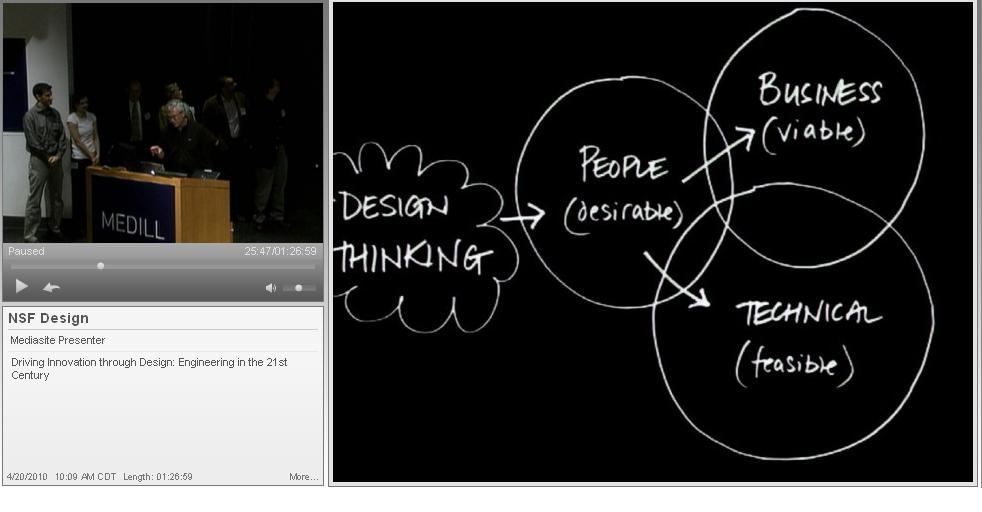
… Although the design brief plays an important role in concept development, there are few resources about how to write one. In general, the design brief is viewed as a competitive advantage and traditionally guarded as a business secret. Research on writing a design brief is scant and prescriptions for how to organize documents are heavily based on individual consultants’ experiences. As such, most design briefs are the writer’s interpretation of a Request For Proposals (RFP) or merely a reformulation of an existing business plan (Petersen 2011)…
… The responsibility for writing a design brief is usually relegated to one department and there is little or no cross-departmental collaboration. At the Industrial Design Society of America event in 2012, for example, design students and professional designers alike voiced their concerns about the design briefs they had seen. The design briefs written by engineering departments contained too much information and were overly restrictive, whereas the design briefs written by marketing departments contained too little information and did not inspire designers. Therefore, many designers read a design brief when a project is started and rarely revisit it afterward…
Table of Contents
1 A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO DESIGN THINKING 1
Michael G. Luchs
PART I: DESIGN THINKING TOOLS 13
2 INSPIRATIONAL DESIGN BRIEFING 15
Søren Petersen, Jaewoo Joo
3 PERSONAS: POWERFUL TOOL FOR DESIGNERS 27
Robert Chen, Jeanny Liu
4 CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE MAPPING: THE SPRINGBOARD TO INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS 41
Jonathan Bohlmann, John McCreery
5 DESIGN THINKING TO BRIDGE RESEARCH AND CONCEPT DESIGN 59
Lauren Weigel
6 BOOSTING CREATIVITY IN IDEA GENERATION USING DESIGN HEURISTICS 71
Colleen M. Seifert, Richard Gonzalez, Seda Yilmaz, Shanna Daly
7 THE KEY ROLES OF STORIES AND PROTOTYPES IN DESIGN THINKING 87
Mark Zeh
PART II: DESIGN THINKING WITHIN THE FIRM 105
8 INTEGRATING DESIGN INTO THE FUZZY FRONT END OF THE INNOVATION PROCESS 107
Giulia Calabretta, Gerda Gemser
9 THE ROLE OF DESIGN IN EARLY-STAGE VENTURES: HOW TO HELP START-UPS UNDERSTAND AND APPLY DESIGN PROCESSES TO NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 125
J. D. Albert
10 DESIGN THINKING FOR NON-DESIGNERS: A GUIDE FOR TEAM TRAINING AND IMPLEMENTATION 143
Victor P. Seidel, Sebastian K. Fixson
11 DEVELOPING DESIGN THINKING: GE HEALTHCARE’S MENLO INNOVATION MODEL 157
Sarah J. S.Wilner
12 LEADING FOR A CORPORATE CULTURE OF DESIGN THINKING 173
Nathan Owen Rosenberg Sr., Marie-Caroline Chauvet, Jon S. Kleinman
13 KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT AS INTELLIGENCE AMPLIFICATION FOR BREAKTHROUGH INNOVATIONS 187
Vadake K. Narayanan, Gina Colarelli O’Connor
14 STRATEGICALLY EMBEDDING DESIGN THINKING IN THE FIRM 205
Pietro Micheli, Helen Perks
PART III: DESIGN THINKING FOR SPECIFIC CONTEXTS 221
15 DESIGNING SERVICES THAT SING AND DANCE 223
Marina Candi, Ahmad Beltagui
16 CAPTURING CONTEXT THROUGH SERVICE DESIGN STORIES 237
KatarinaWetter-Edman, Peter R. Magnusson
17 OPTIMAL DESIGN FOR RADICALLY NEW PRODUCTS 253
Steve Hoeffler, Michal Herzenstein, Tamar Ginzburg
18 BUSINESS MODEL DESIGN 265
John Aceti, Tony Singarayar
19 LEAN START-UP IN LARGE ENTERPRISES USING HUMAN-CENTERED DESIGN THINKING: A NEW APPROACH FOR DEVELOPING TRANSFORMATIONAL AND DISRUPTIVE INNOVATIONS 281
Peter Koen
PART IV: CONSUMER RESPONSES AND VALUES 301
20 CONSUMER RESPONSE TO PRODUCT FORM 303
Mariëlle E. H. Creusen
21 DRIVERS OF DIVERSITY IN CONSUMERS’ AESTHETIC RESPONSE TO PRODUCT DESIGN 319
Adèle Gruen
22 FUTURE-FRIENDLY DESIGN: DESIGNING FOR AND WITH FUTURE CONSUMERS 333
Andy Hines
23 FACE AND INTERFACE: RICHER PRODUCT EXPERIENCES THROUGH INTEGRATED USER INTERFACE AND INDUSTRIAL DESIGN 351
Keith S. Karn
24 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY PROTECTION FOR DESIGNS 367
Daniel Harris Brean
25 DESIGN THINKING FOR SUSTAINABILITY 381
Rosanna Garcia, PhD, Scott Dacko, PhD
- The Huffington Post article about design brief and design thinking by Soren Petersen (“How to Manage Innovation with Design Thinking”)