Many design practitioners aim to enhance the beauty of an existing product or develop novel products and services. However, market does not always pay off their effort. Carefully designed products often fail to attract consumers. What should designers do to enhance sales?

One solution is to borrow insights from behavioral economics. Studies show that behavioral economics can increase the adoption rate of newly designed products because it overcomes consumer resistance.
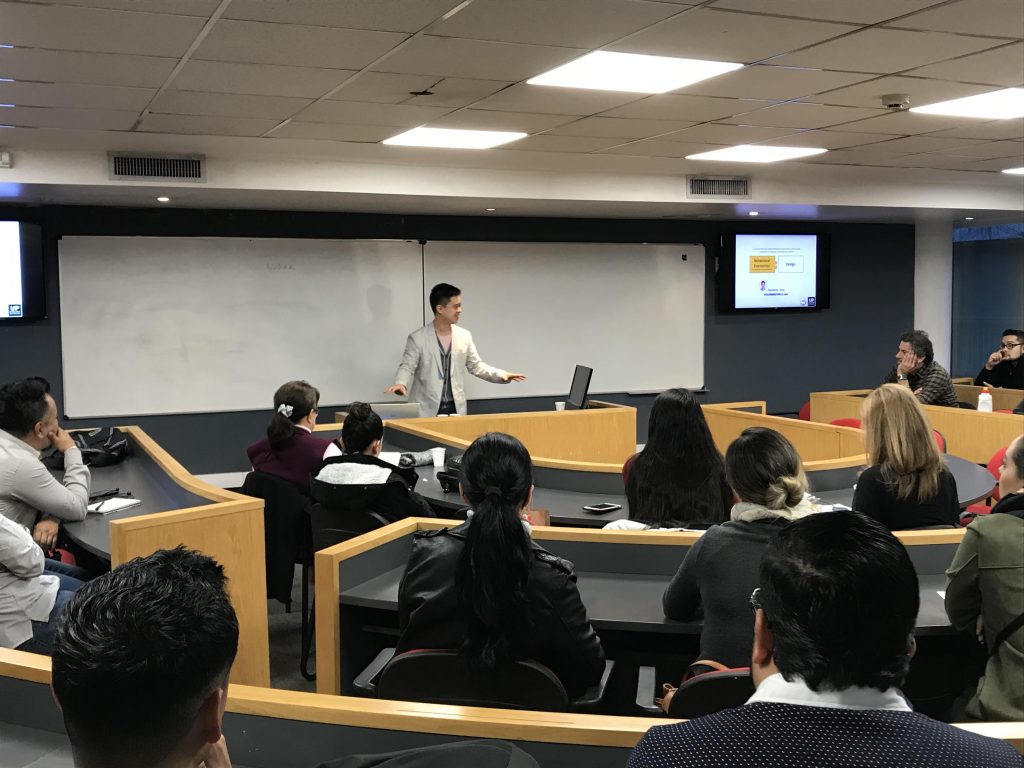
I was once invited by Palermo University in Argentina to share findings about the commercial impact of behavioral economics in the context of design. I shared my experimental findings about three Korean companies.
(1) Samsung’s printer would sell more if its ugly version is placed next to it because joint evaluation helps consumers consider aesthetics importantly,
(2) LG’s Styler would sell more if the clock in the store presents time in analog not in digital because doing so encourages consumers to think abstractly and creatively to appreciate the value of something new, and
(3) SK Telecom’s AI speaker would be used more often if it has a human feature and viewed as a foreigner or child because people become more tolerant about the mistakes of the AI speaker.