At the recent O’Malley School of Business (OMSB) Seminar at Manhattan University, I shared our research on minimalist design. This collaborative work with Yooncheol Shin, then a graduate student at the Techno Design Graduate School at Kookmin University and now a UX researcher at the Customer Experience Center at Woori Bank, explores when simplicity enhances consumer preference, and when it backfires.
We conducted one lab experiment and one field experiment to test a key idea: not all design elements contribute equally to how consumers form their preferences.
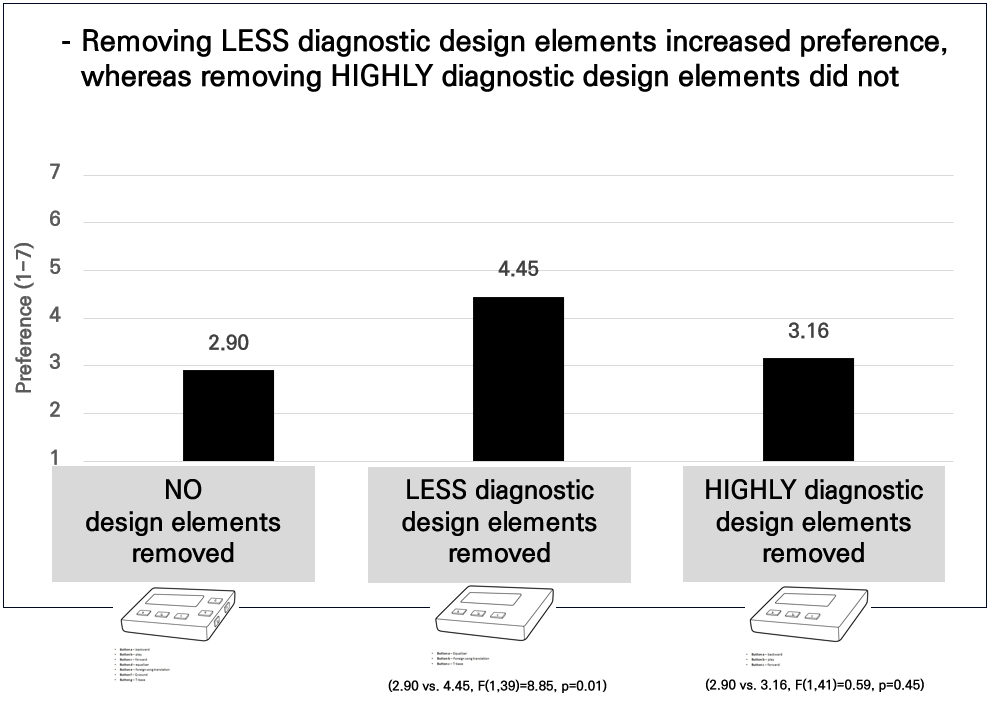
We found that removing LESS diagnostic design elements (e.g., buttons for play, forward, or backward songs) from an MP3 player increased participants’ preference. However, removing HIGHLY diagnostic design elements (e.g., buttons for equalizer, foreign song translation, or T-base) did not produce the same effect.
Our findings challenge the widely accepted “less is more” mantra. By connecting design practice and marketing theory, we offer practical insights for UX designers and brand managers who want to simplify without losing impact.
***
Reference
Pieters, R., Wedel, M., & Batra, R. (2010). The stopping power of advertising: Measures and effects of visual complexity. Journal of Marketing, 74(5), 48–60.
Advertising needs to capture consumers’ attention in likable ways, and the visual complexity of advertising plays a central role in this regard. Yet ideas about visual complexity effects conflict, and objective measures of complexity are rare. The authors distinguish two types of visual complexity, differentiate them from the difficulty of comprehending advertising, and propose objective measures for each. Advertisements are visually complex when they contain dense perceptual features (“feature complexity”) and/or when they have an elaborate creative design (“design complexity”). An analysis of 249 advertisements that were tested with eye-tracking shows that, as the authors hypothesize, feature complexity hurts attention to the brand and attitude toward the ad, whereas design complexity helps attention to both the pictorial and the advertisement as a whole, its comprehensibility, and attitude toward the ad. This is important because design complexity is under direct control of the advertiser. The proposed measures can be readily adopted to assess the visual complexity of advertising, and the findings can be used to improve the stopping power of advertisements.