Bertao, R. A., & Joo, J. (2021). “Hey Alexa, Would You Create a Color Palette?” UX/UI Designers’ Perspectives on Using Natural Language to Interact with Future Intelligent Design Assistants. Journal of The Korea Convergence Society, 12(11), 1–14.
Abstract
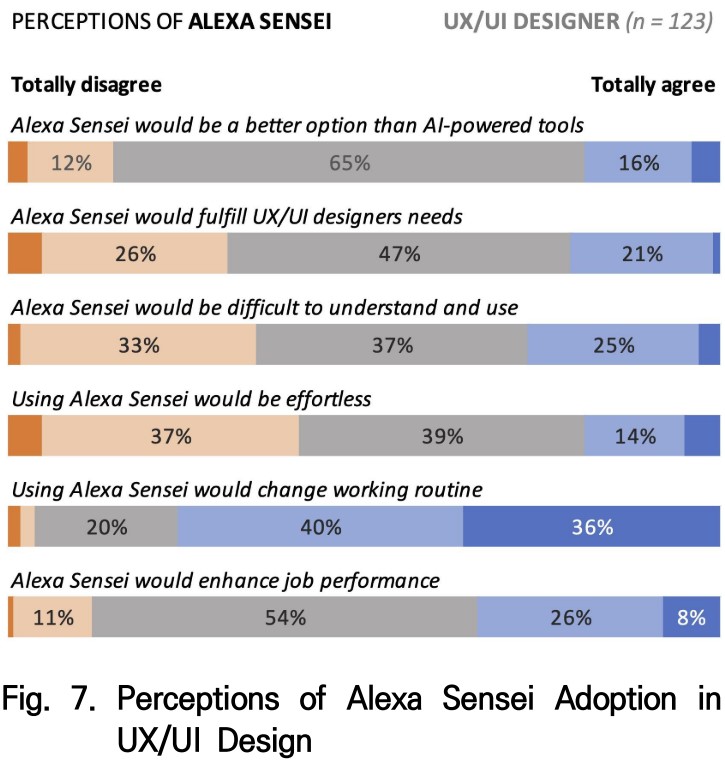
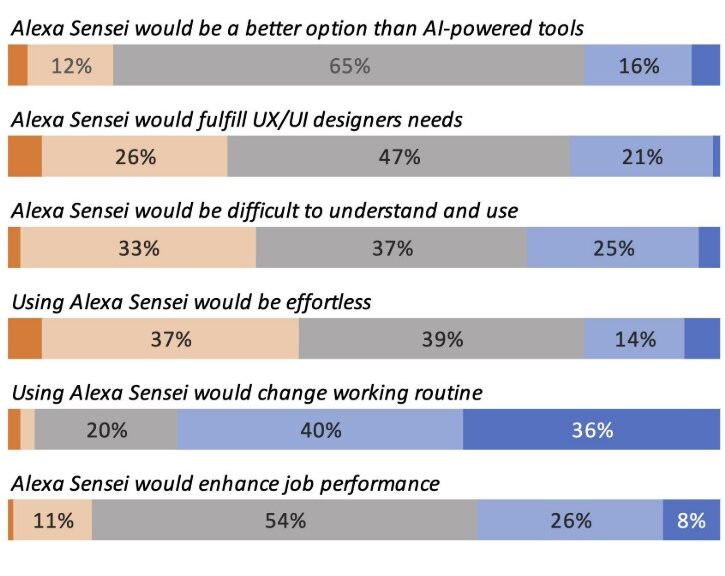
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been inserted into people’s lives through Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVA), like Alexa. Moreover, intelligent systems have expanded to design studios. This research delves into designers’ perspectives on developing AI-based practices and examines the challenges of adopting future intelligent design assistants. We surveyed UX/UI professionals in Brazil to understand how they use IVAs and AI design tools. We also explored a scenario featuring the use of Alexa Sensei, a hypothetical voice-controlled AI-based design assistant mixing Alexa and Adobe Sensei characteristics. The findings indicate respondents have had limited opportunities to work with AI, but they expect intelligent systems to improve the efficiency of the design process. Further, majority of the respondents predicted that they would be able to collaborate creatively with AI design systems. Although designers anticipated challenges in natural language interaction, those who already adopted IVAs were less resistant to the idea of working with Alexa Sensei as an AI design assistant.
Keywords
Artificial intelligence adoption, Artificial intelligence-based design, Intelligent Virtual assistant, Voice interaction, UX/UI design