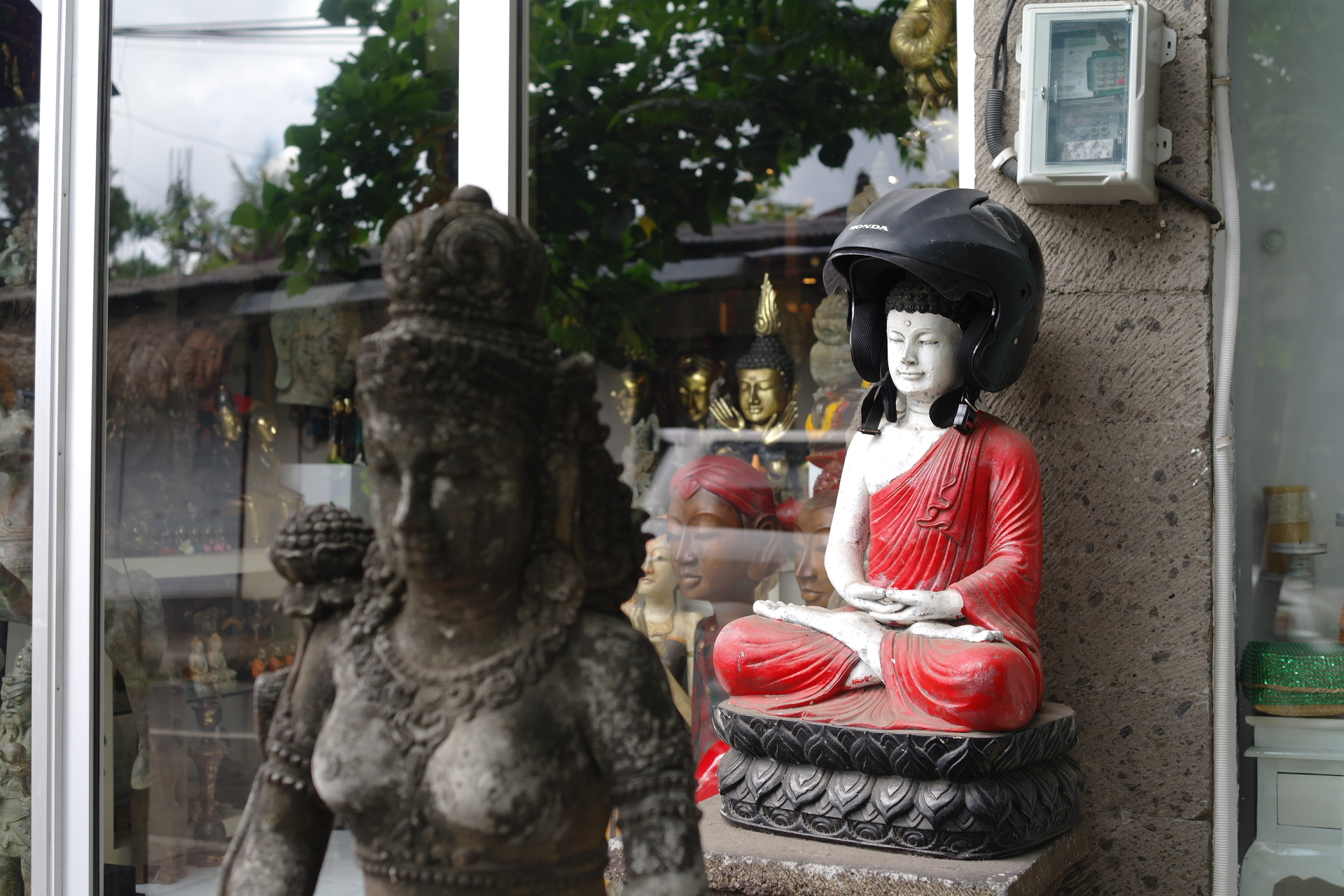
Ubud is a small town on the Indonesian island of Bali. “Eat, Pray, Love” was filmed in 2010 in this town. IMDb explains this movie;
A married woman realizes how unhappy her marriage really is, and that her life needs to go in a different direction. After a painful divorce, she takes off on a round-the-world journey to find herself.
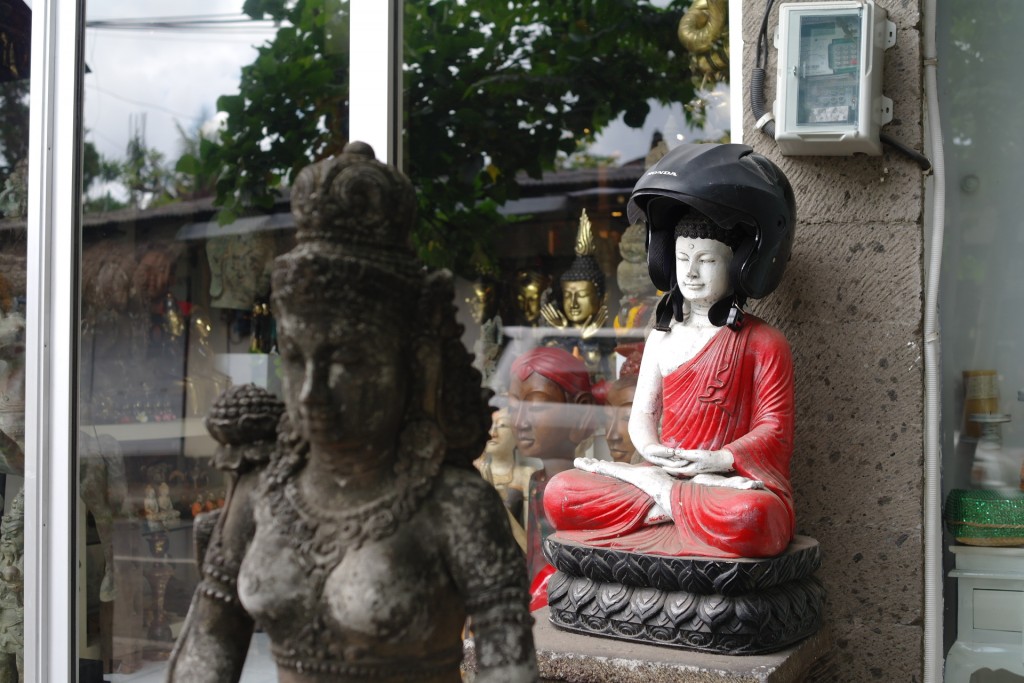

Although not everyone needs to find himself or herself like a person in the movie, Bali is a perfect place to enjoy a mind wandering (taking a break involving an undemanding task) and to be creative. Indeed, in this town, many European visitors read and write books at cafes enjoying rice field views (to my surprise, rice fields can be scenic!). Some even go to a co-working space called Hubud and start their own businesses. I find many do undemanding tasks. Since residents are friendly, meals are delicious (Babi Guling at Ibu Oka), and guest houses are inexpensive, Bali is one of the destinations for those who need creativity.

Reference
Baird, B., Smallwood, J., Mrazek, M. D., Kam, J. W., Franklin, M. S., & Schooler, J. W. (2012). Inspired by distraction: Mind wandering facilitates creative incubation. Psychological science, 23(10), 1117-1122.
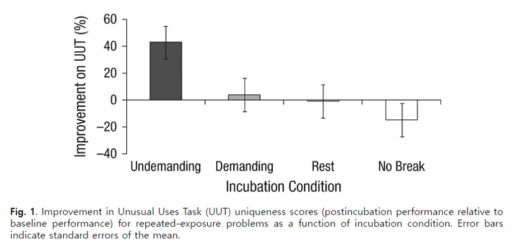
Although anecdotes that creative thoughts often arise when one is engaged in an unrelated train of thought date back thousands of years, empirical research has not yet investigated this potentially critical source of inspiration. We used an incubation paradigm to assess whether performance on validated creativity problems (the Unusual Uses Task, or UUT) can be facilitated by engaging in either a demanding task or an undemanding task that maximizes mind wandering. Compared with engaging in a demanding task, rest, or no break, engaging in an undemanding task during an incubation period led to substantial improvements in performance on previously encountered problems. Critically, the context that improved performance after the incubation period was associated with higher levels of mind wandering but not with a greater number of explicitly directed thoughts about the UUT. These data suggest that engaging in simple external tasks that allow the mind to wander may facilitate creative problem solving.