I have used Southwest Airlines a few times when visiting Las Vegas or Los Angeles. Now I have learned that a small airport like San Jose (SJC) is better than a big one like San Francisco (SFO). My destinations are also local like Long Beach (LGB) or Orange County (SNA) not the big one, Los Angeles (LAX). As I realized that local airports are better than large ones, I felt that Southwest matches that atmosphere well.
I have a memorable experience with Southwest at Long Beach Airport. While the aircraft was being fueled and passengers were boarding, the crew played loud, fun music. It felt very different from other airlines that are usually serious.
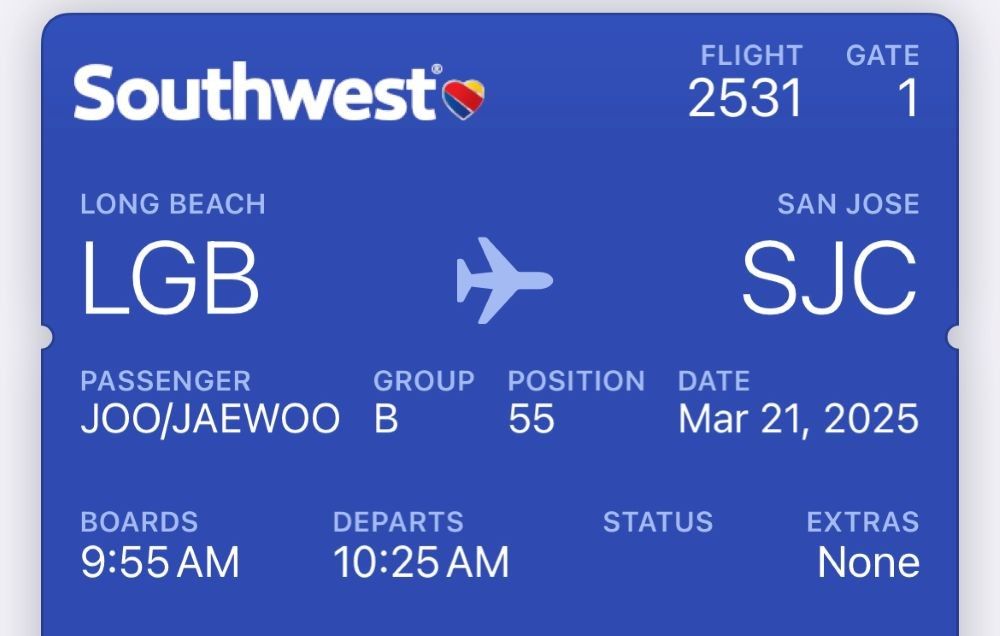

Another interesting about Southwest is its boarding system. There is are seat numbers. Just a group and position is shown on the ticket. At the gate, passengers line up in order. This system seems to make boarding faster.

But the most important part is the airport where Southwest takes off or lands. Small airports are clean, close to downtown, and quiet. They made my Southwest experience feel fresh. If I flew Southwest from big airports like SFO or LAX, I might not feel the same way. Sometimes, the place shapes how we feel about a brand.
***
Reference
O’Guinn, T. C., Tanner, R. J., & Maeng, A. (2015). Turning to space: Social density, social class, and the value of things in stores. Journal of Consumer Research, 42(2), 196–213.
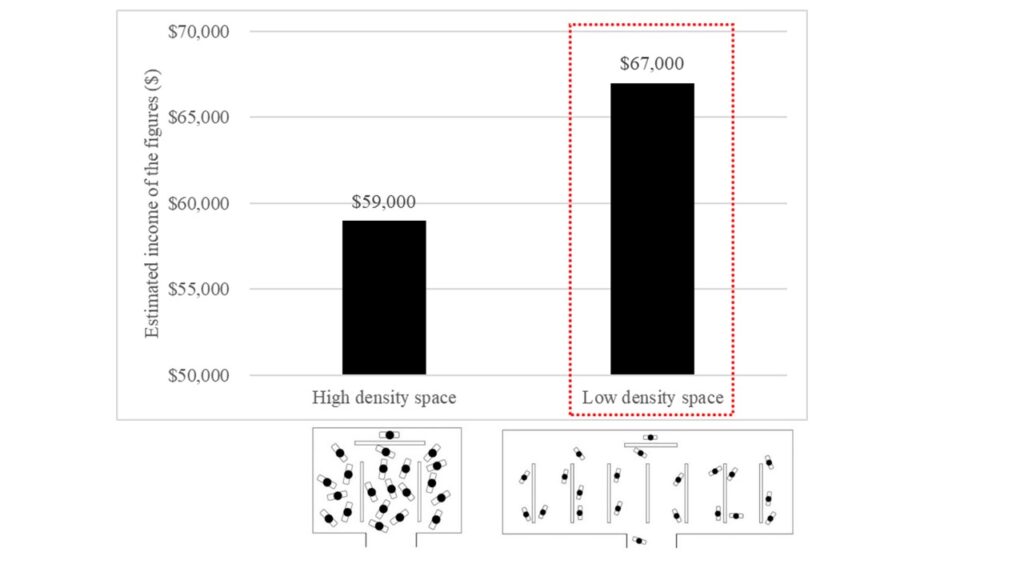
This article is about social space and material objects for sale within that space. We draw primarily on Goffman’s (1971) concepts of use space and possession territories to predict that as the social density of a given space increases, inferences of the subjective social class and income of people in that space fall. Eight studies confirm that this is indeed the case, with the result holding even for stick figures, thus controlling for typical visual indicators of social class such as clothing or jewelry. Furthermore, these social class inferences mediate a relationship between social density and product valuation, with individuals assessing both higher prices and a greater willingness to pay for products presented in less crowded contexts. This effect of inferred class on product valuation is explained by status-motivated individuals’ desire to associate with higher-status people. To the best of our knowledge, this research is the first to reveal the link between social density, status inferences, and object valuations. As such, it makes a novel contribution to what has come to be known in sociology as the topological turn: a renewed focus on social space.