River Thames flows through London. People come to the London Bridge to enjoy the river.

When I visited the London Bridge, there was a pink public litter bin in the beginning of the bridge. Many visitors stopped in front of it momentarily and threw litter away before crossing the bridge.

Although adding human faces or adding controversial messages encourages our prosocial behaviors, adding an opportunity to vote could be another effective intervention. Asking people to vote by splitting a litter bin into two sub bins looks more effective than designing a gigantic litter bin like a disposable coffee cup. I believe libertarian paternalism proposed by behavioral economists could help people behave in a better way.
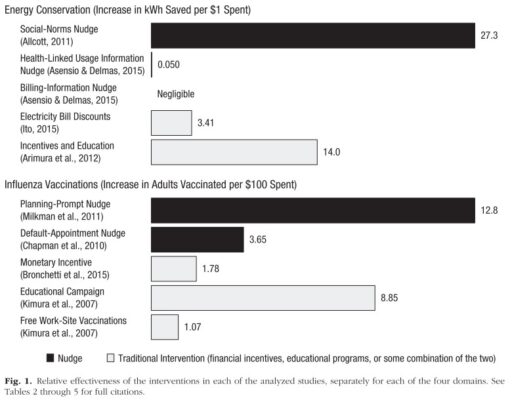
Governments are increasingly adopting behavioral science techniques for changing individual behavior in pursuit of policy objectives. The types of “nudge” interventions that governments are now adopting alter people’s decisions without coercion or significant changes to economic incentives. We calculated ratios of impact to cost for nudge interventions and for traditional policy tools, such as tax incentives and other financial inducements, and we found that nudge interventions often compare favorably with traditional interventions. We conclude that nudging is a valuable approach that should be used more often in conjunction with traditional policies, but more calculations are needed to determine the relative effectiveness of nudging.